The Roles of Auxin Biosynthesis YUCCA Gene Family in Plants
- PMID: 31888214
- PMCID: PMC6941117
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20246343
The Roles of Auxin Biosynthesis YUCCA Gene Family in Plants
Abstract
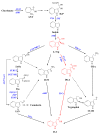
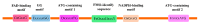
Auxin plays essential roles in plant normal growth and development. The auxin signaling pathway relies on the auxin gradient within tissues and cells, which is facilitated by both local auxin biosynthesis and polar auxin transport (PAT). The TRYPTOPHAN AMINOTRANSFERASE OF ARABIDOPSIS (TAA)/YUCCA (YUC) pathway is the most important and well-characterized pathway that plants deploy to produce auxin. YUCs function as flavin-containing monooxygenases (FMO) catalyzing the rate-limiting irreversible oxidative decarboxylation of indole-3-pyruvate acid (IPyA) to form indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). The spatiotemporal dynamic expression of different YUC gene members finely tunes the local auxin biosynthesis in plants, which contributes to plant development as well as environmental responses. In this review, the recent advances in the identification, evolution, molecular structures, and functions in plant development and stress response regarding the YUC gene family are addressed.
Keywords: YUCCA; auxin; development; local auxin biosynthesis; stress response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 31700527/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31670306/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 17KJB220002/Fundamental Research Program (Natural Science Foundation) of Jiangsu Universities
- 1732931608/Research Fund of Jiangsu University of Science and Technology
- CARS-18/China Agriculture Research System
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

