The Fabrication of Micro/Nano Structures by Laser Machining
- PMID: 31888222
- PMCID: PMC6956144
- DOI: 10.3390/nano9121789
The Fabrication of Micro/Nano Structures by Laser Machining
Abstract
Micro/nano structures have unique optical, electrical, magnetic, and thermal properties. Studies on the preparation of micro/nano structures are of considerable research value and broad development prospects. Several micro/nano structure preparation techniques have already been developed, such as photolithography, electron beam lithography, focused ion beam techniques, nanoimprint techniques. However, the available geometries directly implemented by those means are limited to the 2D mode. Laser machining, a new technology for micro/nano structural preparation, has received great attention in recent years for its wide application to almost all types of materials through a scalable, one-step method, and its unique 3D processing capabilities, high manufacturing resolution and high designability. In addition, micro/nano structures prepared by laser machining have a wide range of applications in photonics, Surface plasma resonance, optoelectronics, biochemical sensing, micro/nanofluidics, photofluidics, biomedical, and associated fields. In this paper, updated achievements of laser-assisted fabrication of micro/nano structures are reviewed and summarized. It focuses on the researchers' findings, and analyzes materials, morphology, possible applications and laser machining of micro/nano structures in detail. Seven kinds of materials are generalized, including metal, organics or polymers, semiconductors, glass, oxides, carbon materials, and piezoelectric materials. In the end, further prospects to the future of laser machining are proposed.
Keywords: application; femtosecond laser; laser machining; material; mental; micro/nano fabrication; micro/nano structures; semiconductor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
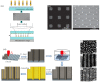
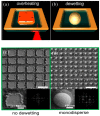
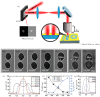
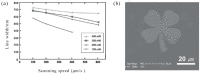
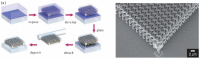
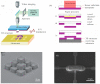


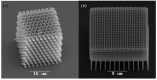
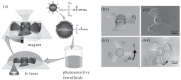

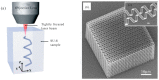
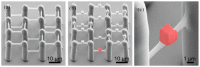
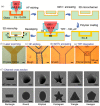
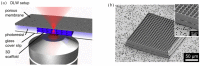
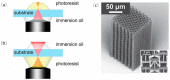
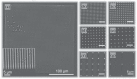
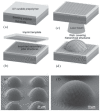
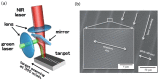
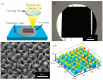
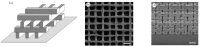

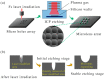
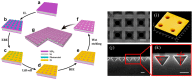
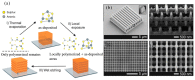
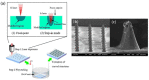
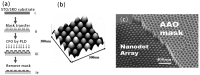
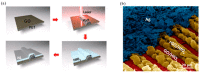
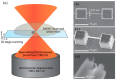
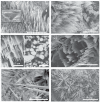
References
-
- Zang X., Zhou Q., Chang J., Liu Y., Lin L. Graphene and carbon nanotube (CNT) in MEMS/NEMS applications. Microelectron. Eng. 2015;132:192–206. doi: 10.1016/j.mee.2014.10.023. - DOI
-
- Archana P., Jose R., Vijila C., Ramakrishna S.J. Improved electron diffusion coefficient in electrospun TiO2 nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2009;113:21538–21542. doi: 10.1021/jp908238q. - DOI
-
- Bhushan B., Jung Y.C. Natural and biomimetic artificial surfaces for superhydrophobicity, self-cleaning, low adhesion, and drag reduction. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2011;56:1–108. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2010.04.003. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

