Role of High-Density Lipoproteins in Cholesterol Homeostasis and Glycemic Control
- PMID: 31888429
- PMCID: PMC6988162
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.119.013531
Role of High-Density Lipoproteins in Cholesterol Homeostasis and Glycemic Control
Keywords: HDL; cholesterol; diabetes mellitus; glycemic control; insulin sensitivity; β‐cell function.
Figures
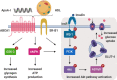
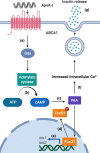

References
-
- Drew BG, Duffy SJ, Formosa MF, Natoli AK, Henstridge DC, Penfold SA, Thomas WG, Mukhamedova N, de Courten B, Forbes JM, Yap FY, Kaye DM, van Hall G, Febbraio MA, Kemp BE, Sviridov D, Steinberg GR, Kingwell BA. High‐density lipoprotein modulates glucose metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2009;119:2103–2111. - PubMed
-
- Barter PJ, Rye KA, Tardif JC, Waters DD, Boekholdt SM, Breazna A, Kastelein JJ. Effect of torcetrapib on glucose, insulin, and hemoglobin A1c in subjects in the Investigation of Lipid Level Management to Understand its Impact in Atherosclerotic Events (ILLUMINATE) trial. Circulation. 2011;124:555–562. - PubMed
-
- Abbasi A, Corpeleijn E, Gansevoort RT, Gans RO, Hillege HL, Stolk RP, Navis G, Bakker SJ, Dullaart RP. Role of HDL cholesterol and estimates of HDL particle composition in future development of type 2 diabetes in the general population: the Prevend Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:E1352–E1359. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt MI, Duncan BB, Bang H, Pankow JS, Ballantyne CM, Golden SH, Folsom AR, Chambless LE. Identifying individuals at high risk for diabetes: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:2013–2018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

