Chronic kidney disease: a review of proteomic and metabolomic approaches to membranous glomerulonephritis, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and IgA nephropathy biomarkers
- PMID: 31889913
- PMCID: PMC6925425
- DOI: 10.1186/s12953-019-0155-y
Chronic kidney disease: a review of proteomic and metabolomic approaches to membranous glomerulonephritis, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and IgA nephropathy biomarkers
Abstract
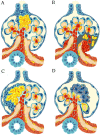
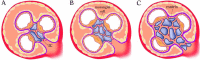
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a global health problem annually affecting millions of people around the world. It is a comprehensive syndrome, and various factors may contribute to its occurrence. In this study, it was attempted to provide an accurate definition of chronic kidney disease; followed by focusing and discussing on molecular pathogenesis, novel diagnosis approaches based on biomarkers, recent effective antigens and new therapeutic procedures related to high-risk chronic kidney disease such as membranous glomerulonephritis, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and IgA nephropathy, which may lead to end-stage renal diseases. Additionally, a considerable number of metabolites and proteins that have previously been discovered and recommended as potential biomarkers of various CKDs using '-omics-' technologies, proteomics, and metabolomics were reviewed.
Keywords: Biomarker; Focal segmental glomerulonephritis; IgA nephropathy; Membranous glomerulonephritis; Proteomics.
© The Author(s). 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Baumgarten M, Gehr T. Chronic kidney disease: detection and evaluation. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84(10):1138. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

