Minimally Invasive Sacroiliac Joint Fusion for the Treatment of Brucella Pyogenic Sacroiliitis: A Case Report
- PMID: 31890413
- PMCID: PMC6925378
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.6212
Minimally Invasive Sacroiliac Joint Fusion for the Treatment of Brucella Pyogenic Sacroiliitis: A Case Report
Abstract
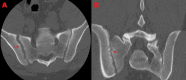
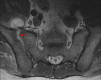
A 39-year-old male presented with a two-month history of right hip pain. Computed tomography (CT) scan demonstrated right sacroiliac joint space widening with cortical destruction and erosive changes in the iliopsoas muscle. Minimally invasive right sacroiliac joint fusion was performed with biopsy and aspirate, which confirmed positive Brucella cultures. The patient was started on long-term antibiotic therapy, and his pain significantly improved. Pyogenic sacroiliitis is a rare condition that requires a high index of suspicion. In this case, minimally invasive sacroiliac joint fusion successfully treated the patient's pain and instability as well as aided in the diagnosis of Brucella infection.
Keywords: brucella; pyogenic sacroiliitis; sacroiliac joint; sacroiliac joint fusion; sacroiliitis.
Copyright © 2019, Anton et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pyogenic infection of the sacroiliac joint. Case reports and review of the literature.Medicine (Baltimore). 1991 May;70(3):188-97. doi: 10.1097/00005792-199105000-00003. Medicine (Baltimore). 1991. PMID: 2030642 Review.
-
Pyomyositis of the iliacus muscle and pyogenic sacroiliitis after sacroiliac joint block -A case report-.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2013 May;64(5):464-8. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2013.64.5.464. Epub 2013 May 24. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2013. PMID: 23741573 Free PMC article.
-
Successful Treatment of Mycobacterium gordonae Sacroiliitis Using a Novel Minimally Invasive Sacroiliac Joint Arthrodesis: A Case Report.JBJS Case Connect. 2016 Jul-Sep;6(3):e55. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.CC.14.00190. JBJS Case Connect. 2016. PMID: 29252632
-
Sacroiliitis and osteomyelitis caused by serotype 3 Streptococcus pneumonia in a previously healthy adult: a case report.Infect Drug Resist. 2018 Aug 3;11:1043-1046. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S160122. eCollection 2018. Infect Drug Resist. 2018. PMID: 30122960 Free PMC article.
-
Pyogenic Sacroiliitis in a 13-Month-Old Child: A Case Report and Literature Review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Oct;94(42):e1581. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001581. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 26496260 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Management of Instability following Pyogenic Sacroiliitis: Technical Case Report.Case Rep Orthop. 2020 Feb 29;2020:3409306. doi: 10.1155/2020/3409306. eCollection 2020. Case Rep Orthop. 2020. PMID: 32181037 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint Pathology Over the Past 10 Years: Review of Scientific Evidence for New Devices for Sacroiliac Joint Fusion.Cureus. 2021 Jun 3;13(6):e15415. doi: 10.7759/cureus.15415. eCollection 2021 Jun. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34249562 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brucella arthritis of the sacro-iliac joint. Porat S, Shapiro M. Infection. 1984;12:205–207. - PubMed
-
- Brucellosis and sacroiliitis: a common presentation of an uncommon pathogen. Priest JR, Low D, Wang C, Bush T. J Am Board Fam Med. 2008;21:158–161. - PubMed
-
- Pyogenic sacroiliitis: diagnosis, management and clinical outcome. Kucera T, Brtkova J, Sponer P, Ryskova L, Popper E, Frank M, Kucerova M. Skeletal Radiol. 2015;44:63–71. - PubMed
-
- A minimally-invasive technique for the treatment of pyogenic sacroiliitis. Giannoudis PV, Tsiridis E. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89:112–114. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
