Superior vena cava reconstruction and implantation of a leadless pacemaker for management of pacemaker-induced superior vena cava syndrome
- PMID: 31890568
- PMCID: PMC6926231
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hrcr.2019.08.005
Superior vena cava reconstruction and implantation of a leadless pacemaker for management of pacemaker-induced superior vena cava syndrome
Keywords: Atrioventricular block; Lead extraction; Leadless pacemaker; Superior vena cava syndrome; Surgical pacemaker implantation.
Figures
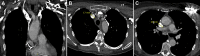

Similar articles
-
Successful implantation of a leadless pacemaker in a patient with complete atrioventricular block and congenital absence of superior vena cava: a case report.Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2021 May 12;5(5):ytab167. doi: 10.1093/ehjcr/ytab167. eCollection 2021 May. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34124567 Free PMC article.
-
Change from Cardioinhibitory Syncope to Iatrogenic Positional Syncope: Superior Vena Cava Syndrome Treated by Superior Vena Cava Stenting and Leadless Pacemaker Implantation.J Innov Card Rhythm Manag. 2018 Sep 15;9(9):3312-3314. doi: 10.19102/icrm.2018.090902. eCollection 2018 Sep. J Innov Card Rhythm Manag. 2018. PMID: 32477822 Free PMC article.
-
Successful implantation of leadless pacemaker in patient with the Günther Tulip inferior vena cava filter.J Cardiol Cases. 2018 Dec 4;19(2):70-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jccase.2018.11.001. eCollection 2019 Feb. J Cardiol Cases. 2018. PMID: 31193668 Free PMC article.
-
[Vena cava superior syndrome: surgical treatment of the thrombosis of the superior vena cava after implantation of a hemodialysis catheter--a case report and review of the literature].Orv Hetil. 2008 Jan 6;149(1):29-34. doi: 10.1556/OH.2008.28207. Orv Hetil. 2008. PMID: 18089480 Review. Hungarian.
-
[The superior vena cava obstruction syndrome after the implantation of a permanent pacemaker: a clinical case report].Cardiologia. 1998 Feb;43(2):201-4. Cardiologia. 1998. PMID: 9557377 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
Leadless pacemakers as a new alternative for pacemaker lead-related superior vena cava syndrome: A case report.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2022 Sep;45(9):1051-1055. doi: 10.1111/pace.14520. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2022. PMID: 35579295 Free PMC article.
-
Benign vena cava superior syndrome in patients with cardiac implantable electronic devices: Presentation and management.HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2020 Sep 15;6(9):549-553. doi: 10.1016/j.hrcr.2020.06.018. eCollection 2020 Sep. HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32983865 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Superior vena cava obstruction and cardiovascular implantable electronic devices-a new era of leadless devices.Mediastinum. 2023 Dec 12;8:1. doi: 10.21037/med-23-33. eCollection 2024. Mediastinum. 2023. PMID: 38322191 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Reynolds D., Duray G.Z., Omar R. A leadless intracardiac transcatheter pacing system. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:533–541. - PubMed
-
- Ruge H., Wildkirt S.M., Poerner M. Severe superior vena cava syndrome after transvenous pacemaker implantation. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;82:e41–e42. - PubMed
-
- Wilkoff B.L., Love C.J., Byrd C.L. Transvenous lead extraction: Heart Rhythm Society expert consensus on facilities, training, indications, and patient management: this document was endorsed by the American Heart Association (AHA) Heart Rhythm. 2009;6:1085–1104. - PubMed
-
- Kusumoto F.M., Schoenfeld M.H., Wilkoff B.L. 2017 HRS expert consensus statement on cardiovascular implantable electronic device lead management and extraction. Heart Rhythm. 2017;14:e503–e551. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

