Distribution and diversity of viruses infecting yams (Dioscorea spp.) in Cameroon
- PMID: 31890752
- PMCID: PMC6917680
- DOI: 10.1007/s13337-019-00552-3
Distribution and diversity of viruses infecting yams (Dioscorea spp.) in Cameroon
Abstract
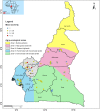
Yam (Dioscorea spp.) is an important food crop cultivated for its edible tubers in Cameroon. Surveys were conducted in Cameroon to determine the incidence and severity of yam mosaic disease and associated viruses in 124 yam farms in four agro-ecological zones in 2014 and 2016. Dioscorea rotundata, D. cayenensis, D. alata, D. Dumetorum and D. bulbifera were most frequently detected yam species in the fields. Symptoms of virus disease were observed on 81.5% of the farms surveyed and the disease incidence ranged from 0 to 96.7%, with an overall mean of 26.5%. Mean symptom severity estimated using a numerical rating scale of 1-5, ranged from 2 to 4.1, with an overall mean of 2.6. Representative set of leaf samples collected from farmers' fields were tested for three viruses known to cause yam mosaic disease in West Africa, viz., Yam mosaic virus (YMV), Yam mild mosaic virus (YMMV) and Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV), using multiplex RT-PCR. YMV and YMMV were detected in 220 (37.2%) of the 591 samples tested and 75% of the farms surveyed. None of the samples tested positive to CMV. Phylogenetic analysis based on the coat protein sequencing of 27 YMV isolates clustered these isolates into three phylogenetic groups. This study demonstrated high prevalence of mosaic disease in yam fields and YMV as main causal agent. Knowledge generated in this study will be useful to augment diagnostic tools and yam mosaic disease control with a view to improve on yam production in Cameroon.
Keywords: Sequence diversity; Viral diseases; Virus diagnostics; Yam virus disease surveys.
© Indian Virological Society 2019.
Figures




References
-
- Abarshi MM, Mohammed IU, Jeremiah SC, Legg JP, Kumar PL, Hillocks RJ, Maruthi MN. Multiplex RT-PCR assays for the detection of both RNA and DNA viruses infecting cassava and the common occurrence of mixed infections by two cassava streak brown streak viruses in east Africa. J Virol Methods. 2012;179:176–184. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2011.10.020. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Adeniji MO, Shoyinka SA, Ikotun T, Asiedu R, Hughes Jd’A, Odu BO. Yield loss in guinea yam (Dioscorea rotundata Poir.) due to infection by Yam mosaic virus (YMV) genus potyvirus. Ife J Sci. 2012;14(2):237–244.
-
- Aleman-Verdageur ME, Goudou-Urbino C, Dubern J, Beachy RN, Fauquet C. Analysis of the sequence diversity of the P1, HC, P3, Nib, and CP genomic regions of several yam mosaic potyvirus isolates: implications for the intra-species molecular diversity of potyviruses. J Gen Virol. 1997;78:1253–1264. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-78-6-1253. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ayisah KD, Gumedzoe YMD. Genetic diversity among Yam mosaic virus (YMV) isolates infecting yam of the complex Dioscorea cayenensis-rotundata in Togo. Int J Biol Chem Sci. 2012;6(3):1090–1101.
-
- Bhattacharjee R, Gedil M, Sartie A, Otoo E, Dumet D, Kikuno H, Kumar PL, Asiedu R. Dioscorea. In: Kole C, editor. Wild crop relatives—genomic and breeding resources, industrial crops. Berlin: Springer; 2011. pp. 71–96.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

