Estrogen activates Alzheimer's disease genes
- PMID: 31890855
- PMCID: PMC6926344
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trci.2019.09.004
Estrogen activates Alzheimer's disease genes
Abstract
Introduction: Women are at increased risk for Alzheimer's disease (AD), but the reason why remains unknown. One hypothesis is that low estrogen levels at menopause increases vulnerability to AD, but this remains unproven.
Methods: We compared neuronal genes upregulated by estrogen in ovariectomized female rhesus macaques with a database of >17,000 diverse gene sets and applied a rare variant burden test to exome sequencing data from 1208 female AD patients with the age of onset < 75 years and 2162 female AD controls.
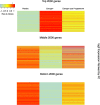
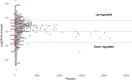
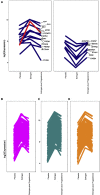
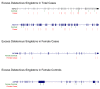
Results: We found a striking overlap between genes upregulated by estrogen in macaques and genes downregulated in the human postmortem AD brain, and we found that estrogen upregulates the APOE gene and that progesterone acts antagonistically to estrogen genome-wide. We also found that female patients with AD have excess rare mutations in the early menopause gene MCM8.
Discussion: We show with genomic data that the menopausal loss of estrogen could underlie the increased risk for AD in women.
Keywords: ABCA7; APOE; ASPM; Estrogen; Genetics; HRT; Hormone replacement therapy; MCM8; Menopause; Mitochondria; SORL1; Women.
© 2019 The Authors.
Figures
References
-
- Andersen K., Launer L.J., Dewey ME, Letenneur L, Ott A, Copeland JR. Gender differences in the incidence of AD and vascular dementia: The EURODEM Studies. EURODEM Incidence Research Group. Neurology. 1999;53:1992–1997. - PubMed
-
- Seshadri S, Wolf PA, Beiser A, Au R, McNulty K, White R. Lifetime risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. The impact of mortality on risk estimates in the Framingham Study. Neurology. 1997;49:1498–1504. - PubMed
-
- Farrer L, Cupples A, Haines J, Hyman B, Kukull W, Mayeux R. Effects of Age, Sex, and Ethnicity on the Association between Apolipoprotein E Genotype and Alzheimer Disease. JAMA. 1997;278:1349–1356. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG033193/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG049508/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003079/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG049505/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102419/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG049507/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG039521/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UF1 AG047133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003273/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG041689/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG049506/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
