Electrical stimulation of the ventral tegmental area evokes sleep-like state transitions under urethane anaesthesia in the rat medial prefrontal cortex via dopamine D1 -like receptors
- PMID: 31891427
- PMCID: PMC7497269
- DOI: 10.1111/ejn.14665
Electrical stimulation of the ventral tegmental area evokes sleep-like state transitions under urethane anaesthesia in the rat medial prefrontal cortex via dopamine D1 -like receptors
Abstract
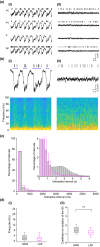
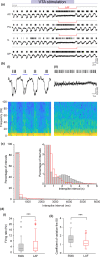
The role of dopamine in regulating sleep-state transitions during, both natural sleep and under anaesthesia, is still unclear. Recording in vivo in the rat mPFC under urethane anaesthesia, we observed predominantly slow wave activity (SWA) of <1 Hz in the local field potential interrupted by occasional spontaneous transitions to a low-amplitude-fast (LAF) pattern of activity. During periods of SWA, transitions to LAF activity could be rapidly and consistently evoked by electrical stimulation of the ventral tegmental area (VTA). Spontaneous LAF activity, and that evoked by stimulation of the VTA, consisted of fast oscillations similar to those seen in the rapid eye movement (REM)-like sleep state. Spontaneous and VTA stimulation-evoked LAF activity occurred simultaneously along the dorsoventral extent of all mPFC subregions. Evoked LAF activity depended on VTA stimulation current and could be elicited using either regular (25-50 Hz) or burst stimulation patterns and was reproducible upon repeated stimulation. Simultaneous extracellular single-unit recordings showed that during SWA, presumed pyramidal cells fired phasically and almost exclusively on the Up state, while during both spontaneous and VTA-evoked LAF activity, they fired tonically. The transition to LAF activity evoked by VTA stimulation depended on dopamine D1 -like receptor activation as it was almost completely blocked by systemic administration of the D1 -like receptor antagonist SCH23390. Overall, our data demonstrate that activation of dopamine D1 -like receptors in the mPFC is important for regulating sleep-like state transitions.
Keywords: Oscillations; REM-like; Up state; slow wave activity.
© 2020 The Authors. European Journal of Neuroscience published by Federation of European Neuroscience Societies and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Medial prefrontal cortical output neurons to the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and their responses to burst-patterned stimulation of the VTA: neuroanatomical and in vivo electrophysiological analyses.Synapse. 1999 Dec 15;34(4):245-55. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2396(19991215)34:4<245::AID-SYN1>3.0.CO;2-D. Synapse. 1999. PMID: 10529719
-
Dorsal vs. ventral differences in fast Up-state-associated oscillations in the medial prefrontal cortex of the urethane-anesthetized rat.J Neurophysiol. 2017 Mar 1;117(3):1126-1142. doi: 10.1152/jn.00762.2016. Epub 2016 Dec 21. J Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28003411 Free PMC article.
-
Differential modulation of anterior cingulate cortical activity by afferents from ventral tegmental area and mediodorsal thalamus.Eur J Neurosci. 2005 Jun;21(11):2975-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04122.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15978009
-
Ventral tegmental area afferents to the prefrontal cortex maintain membrane potential 'up' states in pyramidal neurons via D(1) dopamine receptors.Cereb Cortex. 2000 Dec;10(12):1168-75. doi: 10.1093/cercor/10.12.1168. Cereb Cortex. 2000. PMID: 11073866
-
[Research Progress in the Role of the Ventral Tegmental Area-Medial Prefrontal Cortex Neural Circuit in the Regulation of Arousal].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2024 Jun;46(3):402-408. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.15693. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 38953264 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Similarities and differences between natural sleep and urethane anesthesia.Sci Rep. 2025 May 25;15(1):18270. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01762-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40414876 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D2-receptor neurons in nucleus accumbens regulate sevoflurane anesthesia in mice.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Nov 28;16:1287160. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1287160. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38089676 Free PMC article.
-
Amphetamine Promotes Cortical Up State in Part Via Dopamine Receptors.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 19;12:728729. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.728729. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34489713 Free PMC article.
-
Historical and Modern Evidence for the Role of Reward Circuitry in Emergence.Anesthesiology. 2022 Jun 1;136(6):997-1014. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000004148. Anesthesiology. 2022. PMID: 35362070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The reinstatement of the expression phase of morphine-induced conditioned place preference in male Wistar rats under ventral tegmental area stimulation and brief inactivation.Res Pharm Sci. 2023 Nov 23;18(6):676-695. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.389957. eCollection 2023 Dec. Res Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 39005563 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

