Applications of machine learning in decision analysis for dose management for dofetilide
- PMID: 31891645
- PMCID: PMC6938356
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227324
Applications of machine learning in decision analysis for dose management for dofetilide
Abstract
Background: Initiation of the antiarrhythmic medication dofetilide requires an FDA-mandated 3 days of telemetry monitoring due to heightened risk of toxicity within this time period. Although a recommended dose management algorithm for dofetilide exists, there is a range of real-world approaches to dosing the medication.
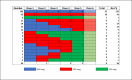
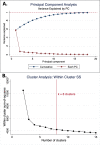
Methods and results: In this multicenter investigation, clinical data from the Antiarrhythmic Drug Genetic (AADGEN) study was examined for 354 patients undergoing dofetilide initiation. Univariate logistic regression identified a starting dofetilide dose of 500 mcg (OR 5.0, 95%CI 2.5-10.0, p<0.001) and sinus rhythm at the start of dofetilide loading (OR 2.8, 95%CI 1.8-4.2, p<0.001) as strong positive predictors of successful loading. Any dose-adjustment during loading (OR 0.19, 95%CI 0.12-0.31, p<0.001) and a history coronary artery disease (OR 0.33, 95%CI 0.19-0.59, p<0.001) were strong negative predictors of successful dofetilide loading. Based on the observation that any dose adjustment was a significant negative predictor of successful initiation, we applied multiple supervised approaches to attempt to predict the dose adjustment decision, but none of these approaches identified dose adjustments better than a probabilistic guess. Principal component analysis and cluster analysis identified 8 clusters as a reasonable data reduction method. These 8 clusters were then used to define patient states in a tabular reinforcement learning model trained on 80% of dosing decisions. Testing of this model on the remaining 20% of dosing decisions revealed good accuracy of the reinforcement learning model, with only 16/410 (3.9%) instances of disagreement.
Conclusions: Dose adjustments are a strong determinant of whether patients are able to successfully initiate dofetilide. A reinforcement learning algorithm informed by unsupervised learning was able to predict dosing decisions with 96.1% accuracy. Future studies will apply this algorithm prospectively as a data-driven decision aid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacologic Conversion during Dofetilide Treatment for Persistent Atrial Fibrillation.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2017 Jun;40(6):667-671. doi: 10.1111/pace.13055. Epub 2017 May 3. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28220940
-
Coronary artery disease potentiates response to dofetilide for rhythm control of atrial fibrillation.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2012 Feb;35(2):170-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.2011.03245.x. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2012. PMID: 22017595
-
Acute conversion of persistent atrial fibrillation during dofetilide loading does not predict long-term atrial fibrillation-free survival.J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2015 Mar;42(2):117-24. doi: 10.1007/s10840-015-9974-7. Epub 2015 Jan 27. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25620152
-
Dofetilide: a new class III antiarrhythmic agent.Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2007 Jan;5(1):9-19. doi: 10.1586/14779072.5.1.9. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2007. PMID: 17187453 Review.
-
Dofetilide: a review of its use in atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter.Drugs. 1999 Dec;58(6):1043-59. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199958060-00007. Drugs. 1999. PMID: 10651390 Review.
Cited by
-
Big Data in electrophysiology.Herzschrittmacherther Elektrophysiol. 2022 Mar;33(1):26-33. doi: 10.1007/s00399-022-00837-z. Epub 2022 Feb 8. Herzschrittmacherther Elektrophysiol. 2022. PMID: 35137276 Review. English.
-
Can additional variables be used to predict stone-free rates following retrograde intrarenal surgery? Anticoagulants and parenchyma thickness: a detailed examination.Urolithiasis. 2023 Jan 11;51(1):30. doi: 10.1007/s00240-022-01404-4. Urolithiasis. 2023. PMID: 36629914
-
Qualitative Evaluation of an Artificial Intelligence-Based Clinical Decision Support System to Guide Rhythm Management of Atrial Fibrillation: Survey Study.JMIR Form Res. 2022 Aug 11;6(8):e36443. doi: 10.2196/36443. JMIR Form Res. 2022. PMID: 35969422 Free PMC article.
-
Postoperative Atrial Fibrillation: A Review.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 1;12(9):1968. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12091968. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A machine learning approach to personalized dose adjustment of lamotrigine using noninvasive clinical parameters.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 10;11(1):5568. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85157-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33692435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alagoz O, Hsu H, Schaefer AJ, Roberts MS. Markov decision processes: a tool for sequential decision making under uncertainty. Medical decision making: an international journal of the Society for Medical Decision Making. 2010;30(4):474–83. Epub 2010/01/02. 10.1177/0272989x09353194 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kaelbling LP, Littman ML, AW. M. Reinforcement Learning: A Survey. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research. 1996;(4):237–85.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

