Autophagy and Macrophage Functions: Inflammatory Response and Phagocytosis
- PMID: 31892110
- PMCID: PMC7016593
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9010070
Autophagy and Macrophage Functions: Inflammatory Response and Phagocytosis
Abstract
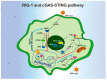
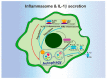
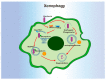
Autophagy is a conserved bulk degradation and recycling process that plays important roles in multiple biological functions, including inflammatory responses. As an important component of the innate immune system, macrophages are involved in defending cells from invading pathogens, clearing cellular debris, and regulating inflammatory responses. During the past two decades, accumulated evidence has revealed the intrinsic connection between autophagy and macrophage function. This review focuses on the role of autophagy, both as nonselective and selective forms, in the regulation of the inflammatory and phagocytotic functions of macrophages. Specifically, the roles of autophagy in pattern recognition, cytokine release, inflammasome activation, macrophage polarization, LC3-associated phagocytosis, and xenophagy are comprehensively reviewed. The roles of autophagy receptors in the macrophage function regulation are also summarized. Finally, the obstacles and remaining questions regarding the molecular regulation mechanisms, disease association, and therapeutic applications are discussed.
Keywords: autophagy; inflammatory response; macrophage; phagocytosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Karanasios E., Walker S.A., Okkenhaug H., Manifava M., Hummel E., Zimmermann H., Ahmed Q., Domart M.-C., Collinson L., Ktistakis N.T. Autophagy initiation by ulk complex assembly on er tubulovesicular regions marked by atg9 vesicles. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:12420. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12420. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

