Pterostilbene Prevents Early Diabetic Retinopathy Alterations in a Rabbit Experimental Model
- PMID: 31892189
- PMCID: PMC7019414
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12010082
Pterostilbene Prevents Early Diabetic Retinopathy Alterations in a Rabbit Experimental Model
Abstract
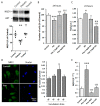
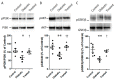
Oxidative stress generated by diabetes plays a key role in the development of diabetic retinopathy (DR), a common diabetic complication. DR remains asymptomatic until it reaches advanced stages, which complicate its treatment. Although it is known that good metabolic control is essential for preventing DR, knowledge of the disease is incomplete and an effective treatment with no side effects is lacking. Pterostilbene (Pter), a natural stilbene with good antioxidant activity, has proved to beneficially affect different pathologies, including diabetes. Therefore, our study aimed to analyse the protective and/or therapeutic capacity of Pter against oxidant damage by characterising early retinal alterations induced by hyperglycaemia, and its possible mechanism of action in a rabbit model of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pter reduced lipid and protein oxidative damage, and recovered redox status and the main activities of antioxidant enzymes. Moreover, the redox regulation by Pter was associated with activation of the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/NRF2 pathway. Our results show that Pter is a powerful protective agent that may delay early DR development.
Keywords: diabetic retinopathy; oxidative stress; polyphenol; pterostilbene; retinal damage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders played no role in: the study design; collections; analyses; data interpretations; writing the manuscript; deciding to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- WHO . Global Report on Diabetes. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2016.
-
- Kisic B., Miric D., Zoric L. Free Radical Biology of Eye Diseases. In: Laher I., editor. Systems Biology of Free Radicals and Antioxidants. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2014. pp. 3599–3623.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

