The Interactions between Ciprofloxacin and Parenteral Nutrition Admixtures
- PMID: 31892212
- PMCID: PMC7023115
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12010027
The Interactions between Ciprofloxacin and Parenteral Nutrition Admixtures
Abstract
Background: Co-infusion of parenteral nutrition (PN) and other drugs increases the risk of the interaction between drug and PN admixtures that can cause embolization of small blood vessels, resulting in potentially fatal consequences, including pulmonary embolism, or liver and retina vascular damage. The present study aimed to determine the compatibility between ciprofloxacin (CF) and eighteen compounded PN admixtures in order to assess the possibility of their co-administration via Y-sites.
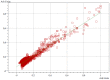
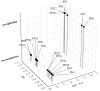
Methods: CF and PN admixtures were mixed at two volume ratios (1:1 and 2:1) and potential interactions were examined using visual inspection, and measurements of pH, osmolality particle size, and zeta potential. The analyses were conducted immediately after sample preparation and after four hours of storage.
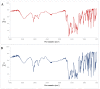
Results: The compatibility tests showed that the addition of the CF to the PN admixtures did not cause any color change or sign of destabilization in the fat emulsion. However, precipitation was observed in formulations containing higher CF concentrations and, in the case of lower CF concentrations, in formulations containing magnesium and calcium ions at a molar ratio of 2:1.
Conclusions: The administration of CF and PN admixtures via the Y-site should be avoided or performed only with PN admixtures for which compatibility has been confirmed and the CF concentration in samples is 1 mg/mL at a molar ratio of magnesium to calcium ions of 1:1.
Keywords: ciprofloxacin; compatibility; drug interactions; parenteral nutrition; zeta potential.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Y-Site Compatibility Studies of Parenteral Nutrition and Other Intravenous Medications in Neonatal and Pediatric Patients: A Review of the Literature Evidence.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Feb 12;16(2):264. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16020264. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38399318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro compatibility studies of vancomycin with ready-to-use parenteral nutrition admixtures for safer clinical practice.Clin Nutr. 2020 Aug;39(8):2539-2546. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2019.11.014. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Clin Nutr. 2020. PMID: 31784302
-
Compatibility of intravenous metronidazole with some all-in-one parenteral nutrition regimens.Nutrition. 2021 Apr;84:111020. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2020.111020. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Nutrition. 2021. PMID: 33139150
-
Co-Administration of Drugs and Parenteral Nutrition: In Vitro Compatibility Studies of Loop Diuretics for Safer Clinical Practice.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Nov 13;12(11):1092. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12111092. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 33202945 Free PMC article.
-
Practical handling of AIO admixtures - Guidelines on Parenteral Nutrition, Chapter 10.Ger Med Sci. 2009 Nov 18;7:Doc18. doi: 10.3205/000077. Ger Med Sci. 2009. PMID: 20049073 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Toward Safe Pharmacotherapy: The Interplay between Meropenem and Parenteral Nutrition Admixtures.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Feb 22;10(2):217. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10020217. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33671502 Free PMC article.
-
Y-Site Compatibility Studies of Parenteral Nutrition and Other Intravenous Medications in Neonatal and Pediatric Patients: A Review of the Literature Evidence.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Feb 12;16(2):264. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16020264. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38399318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Use of Common Administration of Emulsion for Parenteral Nutrition and Vinpocetine: Compatibility Study and Prospect.Metabolites. 2024 Aug 7;14(8):439. doi: 10.3390/metabo14080439. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 39195535 Free PMC article.
-
Electron Beam Radiation as a Safe Method for the Sterilization of Aceclofenac and Diclofenac-The Usefulness of EPR and 1H-NMR Methods in Determination of Molecular Structure and Dynamics.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jun 24;14(7):1331. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14071331. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35890227 Free PMC article.
-
Physicochemical Compatibility of Ceftolozane-Tazobactam with Parenteral Nutrition.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 5;17(7):896. doi: 10.3390/ph17070896. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taxis K., Barber N. Incidence and severity of intravenous drug errors in a German hospital. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004;59:815–817. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

