Design, Synthesis and Molecular Modeling Study of Conjugates of ADP and Morpholino Nucleosides as A Novel Class of Inhibitors of PARP-1, PARP-2 and PARP-3
- PMID: 31892271
- PMCID: PMC6982223
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21010214
Design, Synthesis and Molecular Modeling Study of Conjugates of ADP and Morpholino Nucleosides as A Novel Class of Inhibitors of PARP-1, PARP-2 and PARP-3
Abstract
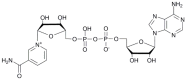
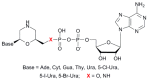
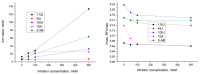
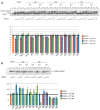
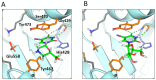
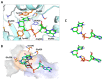
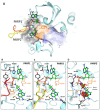
We report on the design, synthesis and molecular modeling study of conjugates of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and morpholino nucleosides as potential selective inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerases-1, 2 and 3. Sixteen dinucleoside pyrophosphates containing natural heterocyclic bases as well as 5-haloganeted pyrimidines, and mimicking a main substrate of these enzymes, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-molecule, have been synthesized in a high yield. Morpholino nucleosides have been tethered to the β-phosphate of ADP via a phosphoester or phosphoramide bond. Screening of the inhibiting properties of these derivatives on the autopoly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of PARP-1 and PARP-2 has shown that the effect depends upon the type of nucleobase as well as on the linkage between ADP and morpholino nucleoside. The 5-iodination of uracil and the introduction of the P-N bond in NAD+-mimetics have shown to increase inhibition properties. Structural modeling suggested that the P-N bond can stabilize the pyrophosphate group in active conformation due to the formation of an intramolecular hydrogen bond. The most active NAD+ analog against PARP-1 contained 5-iodouracil 2'-aminomethylmorpholino nucleoside with IC50 126 ± 6 μM, while in the case of PARP-2 it was adenine 2'-aminomethylmorpholino nucleoside (IC50 63 ± 10 μM). In silico analysis revealed that thymine and uracil-based NAD+ analogs were recognized as the NAD+-analog that targets the nicotinamide binding site. On the contrary, the adenine 2'-aminomethylmorpholino nucleoside-based NAD+ analogs were predicted to identify as PAR-analogs that target the acceptor binding site of PARP-2, representing a novel molecular mechanism for selective PARP inhibition. This discovery opens a new avenue for the rational design of PARP-1/2 specific inhibitors.
Keywords: DNA repair; NAD+ analogs; PARP; molecular modeling; morpholino nucleosides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

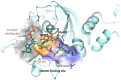
References
-
- Talhaoui I., Lebedeva N.A., Zarkovic G., Saint-Pierre C., Kutuzov M.M., Sukhanova M.V., Matkarimov B.T., Gasparutto D., Saparbaev M.K., Lavrik O.I., et al. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases covalently modify strand break termini in DNA fragments in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:9279–9295. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

