Deletion of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β in D2 Receptor-Positive Neurons Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment via NMDA Receptor-Dependent Synaptic Plasticity
- PMID: 31892408
- PMCID: PMC7103512
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.10.025
Deletion of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β in D2 Receptor-Positive Neurons Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment via NMDA Receptor-Dependent Synaptic Plasticity
Abstract
Background: Cortical dopaminergic systems are critically involved in prefrontal cortex (PFC) functions, especially in working memory and neurodevelopmental disorders such as schizophrenia. GSK-3β (glycogen synthase kinase-3β) is highly associated with cAMP (cyclic adenosine monophosphate)-independent dopamine D2 receptor (D2R)-mediated signaling to affect dopamine-dependent behaviors. However, the mechanisms underlying the GSK-3β modulation of cognitive function via D2Rs remains unclear.
Methods: This study explored how conditional cell-type-specific ablation of GSK-3β in D2R+ neurons (D2R-GSK-3β-/-) in the brain affects synaptic function in the medial PFC (mPFC). Both male and female (postnatal days 60-90) mice, including 140 D2R, 24 D1R, and 38 DISC1 mice, were used.
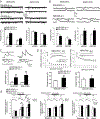
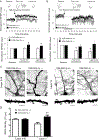
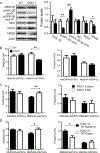
Results: This study found that NMDA receptor (NMDAR) function was significantly increased in layer V pyramidal neurons in mPFC of D2R-GSK-3β-/- mice, along with increased dopamine modulation of NMDAR-mediated current. Consistently, NR2A and NR2B protein levels were elevated in mPFC of D2R-GSK-3β-/- mice. This change was accompanied by a significant increase in enrichment of activator histone mark H3K27ac at the promoters of both Grin2a and Grin2b genes. In addition, altered short- and long-term synaptic plasticity, along with an increased spine density in layer V pyramidal neurons, were detected in D2R-GSK-3β-/- mice. Indeed, D2R-GSK-3β-/- mice also exhibited a resistance of working memory impairment induced by injection of NMDAR antagonist MK-801. Notably, either inhibiting GSK-3β or disrupting the D2R-DISC1 complex was able to reverse the mutant DISC1-induced decrease of NMDAR-mediated currents in the mPFC.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates that GSK-3β modulates cognition via D2R-DISC1 interaction and epigenetic regulation of NMDAR expression and function.
Keywords: Cognition; Dopamine D(2) receptors; Epigenetic; GSK-3β; Histone modification; NMDA receptors; Prefrontal cortex.
Copyright © 2019 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests
The authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

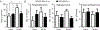
Comment in
-
Epigenetic Mechanism Links NMDA Receptor Hypofunction and Cognitive Deficits in Schizophrenia to D2 Receptors.Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Apr 15;87(8):692-694. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2020.01.024. Biol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32216901 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gee S, Ellwood I, Patel T, Luongo F, Deisseroth K, Sohal VS (2012): Synaptic activity unmasks dopamine D2 receptor modulation of a specific class of layer V pyramidal neurons in prefrontal cortex. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 32:4959–4971. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Seamans JK, Yang CR (2004): The principal features and mechanisms of dopamine modulation in the prefrontal cortex. Prog Neurobiol. 74:1–58. - PubMed
-
- Missale C, Nash SR, Robinson SW, Jaber M, Caron MG (1998): Dopamine receptors: from structure to function. Physiological reviews. 78:189–225. - PubMed
-
- Greengard P (2001): The neurobiology of slow synaptic transmission. Science. 294:1024–1030. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

