Network Pharmacology-Based Study on the Molecular Biological Mechanism of Action for Compound Kushen Injection in Anti-Cancer Effect
- PMID: 31892693
- PMCID: PMC6977710
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.918520
Network Pharmacology-Based Study on the Molecular Biological Mechanism of Action for Compound Kushen Injection in Anti-Cancer Effect
Abstract
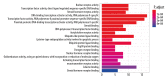
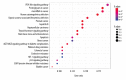
BACKGROUND Compound Kushen injection (CKI) is a traditional Chinese medicine preparation for clinical treatment of cancer pain or treatment of various types of solid tumors. The purpose of this study was to identify the main active compounds from CKI and to investigate its anti-cancer mechanisms via drug target biological network pharmacology construction and prediction. MATERIAL AND METHODS Constituents of CKI were retrieved from Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology (TCMSP) database. Disease targets were collected in the Human Gene (Gene Cards) and Human Mendelian Inheritance (OMIM) databases. "Ingredients-protein targets-pathway" networks were constructed using Cytoscape. STRING database platform to construct enrichment of protein-protein interactions (PPI), related diseases and pathways network. Gene Ontology (GO) biological functions and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway of were performed to investigate by using Bioconductor tool for analysis. RESULTS The results indicated that 60 constituents of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) filtration resulted in 33 constituents exhibiting significant correlations with anti-cancer and CKI may target 113 proteins, including IL6, EGFR, CASP3, VEGFA, MYC, and ESR1. GO and KEGG enrichment analysis results show that 129 biological processes and 93 signal pathways associated with cancer. It mainly involves cancers such as prostate cancer, bladder cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, etc. Active ingredients might also induce apoptosis in cancer cells via the p53 and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway mechanism. CONCLUSIONS This study was based on pharmacological networks results for the prediction of the multi-constituent, multi-target, and multi-pathway mechanisms of CKI, which might be a promising potential therapeutic and prevention candidate for anti-cancer. However, based on computer data mining and analysis, this study still needs to be further verified by in vivo/in vitro experiments, and the safety of CKI needs to be evaluated.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
-
- Ma Y, Gao H, Liu J, et al. Identification and determination of the chemical constituents in a herbal preparation, compound Kushen injection, by HPLC and LC-DAD-MS/MS. Journal of Liquid Chromatography. 2014;37(2):207–20.
-
- Hao G, Zheng J, Huo R, et al. Smilax glabra Roxb targets Akt (p-Thr308) and inhibits Akt-mediated signaling pathways in SGC7901 cells. J Drug Target. 2016;24(6):557–65. - PubMed
-
- Wu CW, Lu L, Liang SW, et al. [Application of drug-target prediction technology in network pharmacology of traditional Chinese medicine]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016;1(3):377–82. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

