Antithrombotic drugs do not increase intraoperative blood loss in emergency gastrointestinal surgery: a single-institution propensity score analysis
- PMID: 31892938
- PMCID: PMC6938014
- DOI: 10.1186/s13017-019-0284-8
Antithrombotic drugs do not increase intraoperative blood loss in emergency gastrointestinal surgery: a single-institution propensity score analysis
Abstract
Background: The use of antithrombotic drugs is increasing with the aging population. Prior to elective procedures, antithrombotic drugs are often discontinued. For emergency procedures in patients taking antithrombotic drugs, their effect cannot be attenuated which may lead to an increased risk of hemorrhagic events. However, there are few studies showing increased intraoperative blood loss in patients taking antithrombotic drugs who undergo emergency gastrointestinal surgery. The aim of this study is to determine whether the use of antithrombotic agents increases intraoperative blood loss in emergency gastrointestinal surgery.
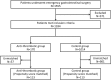
Methods: A retrospective review of patients who underwent emergency abdominal surgery between January 2013 and December 2017 was conducted. The primary outcome measure was intraoperative blood loss. Patients were divided into the antithrombotic drug group and a control group, and a propensity score was developed using multivariate logistic regression. We use 1:1 propensity score matching analysis to compare outcomes between the two groups.
Results: Of 1555 patients included in this study, 1184 patients, including 170 patients taking antithrombotic drugs, were eligible for propensity score matching analysis. A 1:1 matching yielded 117 well-balanced pairs. There was no statistically significant difference in intraoperative blood loss (antithrombotic drug group vs control group, median (interquartile): 60 (225-10) vs 100 (243-10) ml, p = 0.43).
Conclusions: This study suggests that antithrombotic drugs do not increase intraoperative blood loss in patients undergoing emergency gastrointestinal surgery. Emergency gastrointestinal surgery for patients currently taking antithrombotic drugs can be performed safely, and the use of antithrombotic drugs is not a reason to delay surgical intervention.
Keywords: Antithrombotic drug; Emergency gastrointestinal surgery; Intraoperative blood loss.
© The Author(s). 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emergency gastrointestinal surgery in patients undergoing antithrombotic therapy in a single general hospital: a propensity score-matched analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2021 Aug 21;21(1):323. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01897-0. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34418977 Free PMC article.
-
Antithrombotic drugs have a minimal effect on intraoperative blood loss during emergency surgery for generalized peritonitis: a nationwide retrospective cohort study in Japan.World J Emerg Surg. 2021 May 27;16(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s13017-021-00374-z. World J Emerg Surg. 2021. PMID: 34044868 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Continued Administration of Low-dose Aspirin for Intraoperative Bleeding Control in Gastric Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection.Digestion. 2019;100(2):139-146. doi: 10.1159/000494250. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Digestion. 2019. PMID: 30513522
-
Cardiac surgery in patients on antiplatelet and antithrombotic agents.Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005 Spring;17(1):66-72. doi: 10.1053/j.semtcvs.2005.01.001. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005. PMID: 16104363 Review.
-
A Multidisciplinary Approach on the Perioperative Antithrombotic Management of Patients With Coronary Stents Undergoing Surgery: Surgery After Stenting 2.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2018 Mar 12;11(5):417-434. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2017.10.051. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2018. PMID: 29519377 Review.
Cited by
-
Is emergency gastrointestinal system tumor surgery safe under treatment of antitrombotics?Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2022 Jun;28(6):776-780. doi: 10.14744/tjtes.2022.92442. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2022. PMID: 35652882 Free PMC article.
-
Safety of urgent surgery for the patients with proximal femur fracture treated with platelet aggregation inhibitors: a propensity-score matching analysis.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2024 Apr;50(2):347-358. doi: 10.1007/s00068-023-02368-9. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2024. PMID: 37768385
-
Emergency gastrointestinal surgery in patients undergoing antithrombotic therapy in a single general hospital: a propensity score-matched analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2021 Aug 21;21(1):323. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01897-0. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34418977 Free PMC article.
-
Antithrombotic drugs have a minimal effect on intraoperative blood loss during emergency surgery for generalized peritonitis: a nationwide retrospective cohort study in Japan.World J Emerg Surg. 2021 May 27;16(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s13017-021-00374-z. World J Emerg Surg. 2021. PMID: 34044868 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, Buroker AB, Goldberger ZD, Hahn EJ, et al. 2019 ACC/AHA guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140:e563–ee95. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kernan WN, Ovbiagele B, Black HR, Bravata DM, Chimowitz MI, Ezekowitz MD, et al. Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2014;45:2160–2236. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000024. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gerhard-Herman MD, Gornik HL, Barrett C, Barshes NR, Corriere MA, Drachman DE, et al. 2016 AHA/ACC guideline on the management of patients with lower extremity peripheral artery disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2017;135:e726–ee79. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources