HIF-1α Promotes the Metastasis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Targeting SP1
- PMID: 31892989
- PMCID: PMC6930417
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.35537
HIF-1α Promotes the Metastasis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Targeting SP1
Abstract
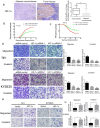
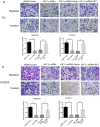
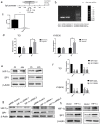
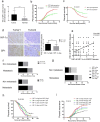
Background: In microenvironment of malignant tumors, Hypoxia-Inducible Factors (HIF), most importantly HIF-1α, play an important role in regulation of adaptive biological response to hypoxia, promoting angiogenesis and metastasis. However, the underlying mechanism that HIF-1α regulates metastasis needs to be further clarified. Methods: The expressions of HIF-1α and SP1 were detected in 182 samples of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and adjacent normal tissues by immunohistochemistry (IHC), and the correlation between the expression levels of HIF-1α and SP1 was analyzed. The expression of HIF-1α in ESCC cell lines TE1 and KYSE30 was then detected using qRT-PCR and western blot. The potential binding sites of HIF-1α on the SP1 promoter were analyzed using UCSC and JASPAR databases, verified by chromosomal immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay and qRT-PCR. The effects of HIF-1α and SP1 on ESCC cell migration and invasion were then tested with Transwell and Matrigel experiments. Results: The expression of HIF-1α in cancer tissues is higher than adjacent normal tissues, and is correlated with metastasis, recurrence and poor prognosis. Upon silencing HIF-1α by siRNA, the invasion and migration ability of ESCC cells were significantly inhibited, which could be restored by the overexpression of SP1. Hypoxic conditions significantly increased the expression of HIF-1α and SP1 at both protein and mRNA levels in ESCC cells. HIF-1α enhanced SP1 transcription through binding to the promoter region. The expression of protein and mRNA levels of SP1 was decreased by silencing HIF-1α in cells. In contrast, overexpression of HIF-1α significantly increased the mRNA and protein levels of SP1. The expression of SP1 in ESCC was positively correlated with the protein expression of HIF-1α and poor prognosis. Conclusion: The results of our study indicate that HIF-1α promotes metastasis of ESCC by targeting SP1 in a hypoxic microenvironment. Further study on this mechanism may elucidate the possibility of HIF-1α and SP1 as new targets for the treatment of ESCC.
Keywords: ESCC; HIF-1α; SP1; tumor metastasis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, Barber RM. et al. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:524–8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL. et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Sjoquist KM, Burmeister BH, Smithers BM. et al. Survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy for resectable oesophageal carcinoma: an updated meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:681–92. - PubMed
-
- Fakhrian K, Ordu AD, Lordick F. et al. Long-term outcomes of trimodality treatment for squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus with cisplatin and/or 5-FU. StrahlentherOnkol. 2014;190:1133–40. - PubMed
-
- Mariette C, Piessen G, Triboulet JP. Therapeutic strategies in oesophageal carcinoma: Role of surgery and other modalities. The Lancet Oncology. 2007;8:545–53. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

