Respiratory syncytial virus in the Western Pacific Region: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 31893034
- PMCID: PMC6925967
- DOI: 10.7189/jogh.09.020431
Respiratory syncytial virus in the Western Pacific Region: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the leading cause of viral pneumonia and bronchiolitis, especially in younger children. The burden of RSV infection in adults, particularly in the older age group, is increasingly recognised. However, RSV disease burden and molecular epidemiology in the World Health Organization (WHO) Western Pacific Region (WPR) has not been reviewed systematically. The aim of this systematic review is to investigate the epidemiological aspects of RSV (incidence, prevalence, seasonality and hospitalisation status) and the associated molecular data in the WPRO countries.
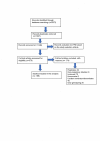
Methods: A systematic search was conducted in international literature databases (MEDLINE, EMBASE, Scopus and Web of Science) to identify RSV-related publications from January 2000 to October 2017 in the WPR countries.
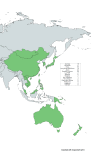
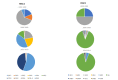
Results: A total of 196 studies from 15 WPR countries were included. The positivity rate for RSV among respiratory tract infection patients was 16.73% (95% confidence interval (CI) = 15.12%-18.4%). The RSV-positive cases were mostly found in hospitalised compared with outpatients (18.28% vs 11.54%, P < 0.001), and children compared with adults (20.72% vs 1.87%, P < 0.001). The seasonality of RSV in the WPR countries follows the latitude, with the peak of RSV season occurring in the winter in temperate countries, and during the rainy season in tropical countries. The molecular epidemiology pattern of RSV in WPR countries was similar to the global pattern, with NA1 (RSV A) and BA (RSV B) being the predominant genotypes.
Conclusions: The available data on RSV are limited in several countries within the WPR, with most data focusing on children and hospitalised patients. Further studies and surveillance, incorporating laboratory testing, are needed to determine the burden of RSV infection in the WPR countries.
Copyright © 2019 by the Journal of Global Health. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest: All authors have completed the Unified Competing Interest form at www.icmje.org/coi_disclosure.pdf (available on request from the corresponding author) and declare no conflicts interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shi T, McAllister DA, O’Brien KL, Simoes EAF, Madhi SA, Gessner BD, et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children in 2015: a systematic review and modelling study. Lancet. 2017;390:946-58. 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30938-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2095-128. 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
