Integrative genomics reveal a role for MCPIP1 in adipogenesis and adipocyte metabolism
- PMID: 31893310
- PMCID: PMC7658075
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-019-03434-5
Integrative genomics reveal a role for MCPIP1 in adipogenesis and adipocyte metabolism
Abstract
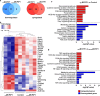
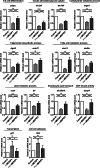
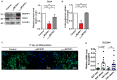
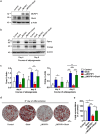
Obesity is considered a serious chronic disease, associated with an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1-induced protein-1 (MCPIP1) is an RNase decreasing stability of transcripts coding for inflammation-related proteins. In addition, MCPIP1 plays an important role in the regulation of adipogenesis in vitro by reducing the expression of key transcription factors, including C/EBPβ. To elucidate the role of MCPIP1 in adipocyte biology, we performed RNA-Seq and proteome analysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes overexpressing wild-type (WTMCPIP1) and the mutant form of MCPIP1 protein (D141NMCPIP1). Our RNA-Seq analysis followed by confirmatory Q-RT-PCR revealed that elevated MCPIP1 levels in 3T3-L1 adipocytes upregulated transcripts encoding proteins involved in signal transmission and cellular remodeling and downregulated transcripts of factors involved in metabolism. These data are consistent with our proteomic analysis, which showed that MCPIP1 expressing adipocytes exhibit upregulation of proteins involved in cellular organization and movement and decreased levels of proteins involved in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. Moreover, MCPIP1 adipocytes are characterized by decreased level of insulin receptor, reduced insulin-induced Akt phosphorylation, as well as depleted Glut4 level and impaired glucose uptake. Overexpression of Glut4 in 3T3-L1 cells expressed WTMCPIP1 rescued adipogenesis. Interestingly, we found decreased level of MCPIP1 along with an increase in body mass index in subcutaneous adipose tissue. The presented data show a novel role of MCPIP1 in modulating insulin sensitivity in adipocytes. Overall, our findings demonstrate that MCPIP1 is an important regulator of adipogenesis and adipocyte metabolism.
Keywords: C/EBPα; Lipid homeostasis; Pparγ; Regnase-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. These experiments are performed according to law of EU.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

