Prevention of tuberculosis in macaques after intravenous BCG immunization
- PMID: 31894150
- PMCID: PMC7015856
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1817-8
Prevention of tuberculosis in macaques after intravenous BCG immunization
Abstract
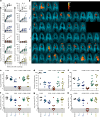
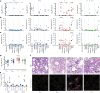
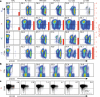
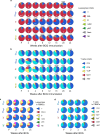
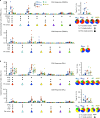
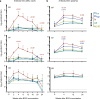
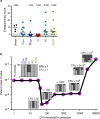
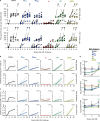
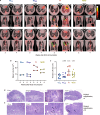
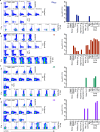
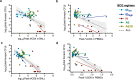
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) is the leading cause of death from infection worldwide1. The only available vaccine, BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guérin), is given intradermally and has variable efficacy against pulmonary tuberculosis, the major cause of mortality and disease transmission1,2. Here we show that intravenous administration of BCG profoundly alters the protective outcome of Mtb challenge in non-human primates (Macaca mulatta). Compared with intradermal or aerosol delivery, intravenous immunization induced substantially more antigen-responsive CD4 and CD8 T cell responses in blood, spleen, bronchoalveolar lavage and lung lymph nodes. Moreover, intravenous immunization induced a high frequency of antigen-responsive T cells across all lung parenchymal tissues. Six months after BCG vaccination, macaques were challenged with virulent Mtb. Notably, nine out of ten macaques that received intravenous BCG vaccination were highly protected, with six macaques showing no detectable levels of infection, as determined by positron emission tomography-computed tomography imaging, mycobacterial growth, pathology and granuloma formation. The finding that intravenous BCG prevents or substantially limits Mtb infection in highly susceptible rhesus macaques has important implications for vaccine delivery and clinical development, and provides a model for defining immune correlates and mechanisms of vaccine-elicited protection against tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors from University of Pittsburgh, NIH and MIT have no competing interests. A.B. is currently an employee of Vir Biotechnology, Inc., which is developing a CMV-based vaccine candidate for TB.
Figures






Comment in
-
Tuberculosis vaccine finds an improved route.Nature. 2020 Jan;577(7788):31-32. doi: 10.1038/d41586-019-03597-y. Nature. 2020. PMID: 31894152 No abstract available.
-
The trick that could inject new life into an old tuberculosis vaccine.Nature. 2020 Jan;577(7789):145. doi: 10.1038/d41586-020-00003-w. Nature. 2020. PMID: 31911698 No abstract available.
-
Routemaps for Highly Effective Tuberculosis Vaccination.Immunity. 2020 Feb 18;52(2):219-221. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.01.017. Immunity. 2020. PMID: 32075726 Free PMC article.
-
Renewing the Fight Against TB with an Old Vaccine.Cell. 2020 Mar 5;180(5):829-831. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.024. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32142676
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Reporthttps://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/ (2018).
-
- Mangtani, P. et al. Protection by BCG vaccine against tuberculosis: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 58, 470–480 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

