Pain relieving effect of dexmedetomidine in patients undergoing total knee or hip arthroplasty: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 31895790
- PMCID: PMC6946532
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018538
Pain relieving effect of dexmedetomidine in patients undergoing total knee or hip arthroplasty: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of dexmedetomidine in patients undergoing total knee and hip arthroplasty for postoperative pain control.
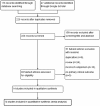
Methods: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) identified in systematic searches of MEDLINE, EMBASE, Google Scholar, the Cochrane Database and the Chinese SinoMed Database.
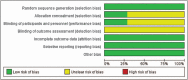
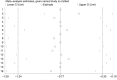
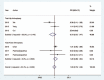
Results: Fourteen RCTs with a total of 1220 patients were included. Overall, dexmedetomidine therapy was associated with significantly decreased pain scores 24 hours after surgery (WMD, -0.36; 95% CI, -0.49 to -0.22; I = 90.0%, P < .001) compared with scores in the control group after total hip arthroplasty (THA) and total knee arthroplasty (TKA). Furthermore, the rate of postoperative delirium was also markedly decreased with dexmedetomidine therapy (RR, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.24 to 0.59; I = 0.0%, P < .001). Moreover, compared with the control group, dexmedetomidine treatment was associated with a decreased risk of postoperative nausea and vomiting in patients undergoing TKA (RR, 0.34; 95% CI, 0.15 to 0.79; I = 0.0%, P = .012), and there was a similar risk of hypotension (RR, 1.03; 95% CI, 0.72 to 1.49; I = 24.4%, P = .87) regardless of whether patients underwent TKA or THA. However, the rate of bradycardia was significantly increased with dexmedetomidine treatment in those undergoing TKA (RR, 6.11; 95% CI, 2.35 to 15.91; I = 0.0%, P < .001).
Conclusions: Dexmedetomidine therapy seems to be an effective treatment for pain control and postoperative delirium in patients undergoing TKA/THA. However, the incidence of bradycardia is markedly increased in patients undergoing TKA. Hence, much larger prospective clinical studies are warranted to confirm these findings.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors state that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Grosu I, Lavand’homme P, Thienpont E. Pain after knee arthoplasty: an unresolved issue. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthosc 2014;22:1744–58. - PubMed
-
- Aveline C, Roux AL, Hetet HL, et al. Pain and recovery after total knee arthoplasty: a 12-month follow-up after a prospective randomized study evaluating Nefopam and Ketamine for early rehabilitation. Clin J Pain 2014;30:749–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

