Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Endovascular Infection in a Neonate: Prolonged, Safe, and Effective Use of Daptomycin and Enoxaparin
- PMID: 31897079
- PMCID: PMC6938295
- DOI: 10.5863/1551-6776-25.1.68
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Endovascular Infection in a Neonate: Prolonged, Safe, and Effective Use of Daptomycin and Enoxaparin
Abstract
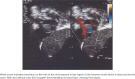
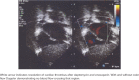
We report on a former 28-week gestation neonate with persistent methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) endocarditis, with a heterozygous Factor V Leiden mutation. The neonate became clinically ill after 1 week of life, with positive blood cultures for MRSA. Echocardiography revealed large thrombi in the inferior vena cava and right atrium. Bacteremia persisted despite removal of umbilical arterial and venous catheters and empiric administration of therapeutic doses of vancomycin (minimum inhibitory concentration [MIC] 2 mg/L) and ceftazidime. To narrow therapy, ceftazidime was discontinued, while gentamicin and rifampin were added. Cultures remained positive and, therefore, linezolid was added, and subsequent blood cultures became negative. Since prolonged linezolid use of 2 weeks or longer carries potential adverse effects, antibiotics were changed to daptomycin, which is bactericidal and recommended for treatment of invasive MRSA infections when vancomycin MICs are ≥2 mg/L to minimize vancomycin treatment failure. Enoxaparin was initiated, with anti-Xa assay monitoring. A workup for thrombophilia revealed heterozygous Factor V Leiden mutation. Serial echocardiograms demonstrated decreasing size of the thrombi, which were no longer visualized at 2 months of age. Creatinine kinase remained normal. The infant had no seizures on daptomycin. The management of persistent MRSA bacteremia in neonates associated with a large thrombus poses a unique challenge due to the long duration of treatment. To our knowledge, this is the first case of prolonged and safe daptomycin and enoxaparin use in a preterm neonate. Daptomycin may be considered in cases of clinical failure with vancomycin when a lengthy treatment course is contemplated.
Keywords: MRSA; daptomycin; endovascular infection; enoxaparin; neonate.
Copyright Published by the Pediatric Pharmacy Association. All rights reserved. For permissions, mhelms@pediatricpharmacy.org 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors declare no conflicts or financial interest in any product or service mentioned in the manuscript, including grants, equipment, medications, employment, gifts, and honoraria. The authors had full access to all patient information in this report and take responsibility for the integrity and accuracy of the report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Successful treatment of daptomycin-nonsusceptible methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia with the addition of rifampin to daptomycin.Ann Pharmacother. 2010 May;44(5):918-21. doi: 10.1345/aph.1M665. Epub 2010 Mar 30. Ann Pharmacother. 2010. PMID: 20354160
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus prosthetic aortic valve endocarditis with paravalvular abscess treated with daptomycin.Heart Lung. 2005 Jan-Feb;34(1):69-71. doi: 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2004.07.009. Heart Lung. 2005. PMID: 15647736
-
In vitro activity of linezolid, tigecycline, and daptomycin on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus blood isolates from adult patients, 2006-2008: stratified analysis by vancomycin MIC.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2011 Oct;44(5):346-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2011.01.037. Epub 2011 Jan 20. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2011. PMID: 21524980
-
Bacteremia due to Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: New Therapeutic Approaches.Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2016 Jun;30(2):491-507. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2016.02.009. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2016. PMID: 27208769 Review.
-
Use of daptomycin to treat infections with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates having vancomycin minimum inhibitory concentrations of 1.5 to 2 μg/mL.Ann Pharmacother. 2013 Dec;47(12):1654-65. doi: 10.1177/1060028013508272. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Ann Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 24259618 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Epidemiology Clinical Manifestations, Decolonization Strategies, and Treatment Options of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection in Neonates.Pathogens. 2025 Feb 5;14(2):155. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14020155. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40005530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
cydA, spdC, and mroQ are novel genes involved in the plasma coagulation of Staphylococcus aureus.Microbiol Immunol. 2021 Sep;65(9):383-391. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12922. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Microbiol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34050992 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics and antibiotic resistance profile of invasive MRSA infections in newborn inpatients: a retrospective multicenter study from China.BMC Pediatr. 2023 May 25;23(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12887-023-04084-0. BMC Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37231456 Free PMC article.
-
Daptomycin Use for Persistent Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcal Bacteremia in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Mar 12;13(3):254. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13030254. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38534689 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Options and Outcomes for the Treatment of Children with Gram-Positive Bacteria with Resistances of Concern: A Systematic Review.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Jan 28;12(2):261. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12020261. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830174 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rimensberger PC, Humbert JR, Beghetti M. Management of preterm infants with intracardiac thrombi: use of thrombolytic agents. Paediatr Drugs. 2001;3(12):883–898. - PubMed
-
- García-Teresa MA, Casado-Flores J, Delgado Domínguez MA et al. Infectious complications of percutaneous central venous catheterization in pediatric patients: a Spanish multicenter study. Intensive Care Med. 2007;33(3):466–476. - PubMed
-
- Chander A, Nagel K, Wiernikowski J et al. Evaluation of the use of low-molecular-weight heparin in neonates: a retrospective, single-center study. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2013;19(5):488–493. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources