Effectiveness and safety of common therapeutic drugs for refractory lupus nephritis: A network meta-analysis
- PMID: 31897105
- PMCID: PMC6923745
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.8257
Effectiveness and safety of common therapeutic drugs for refractory lupus nephritis: A network meta-analysis
Abstract
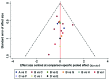
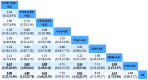
Previous studies have indicated that various drugs may be beneficial for the treatment of patients with refractory lupus nephritis (RLN). The present study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of common therapeutic drugs for the treatment of RLN using a network meta-analysis (NMA). NMA was performed using Stata 14.0 software. The odds ratio (OR) and 95% CI were calculated. A total of 19 studies comprising 1,127 patients were included. Common therapeutic drugs for RLN included glucocorticoids (GC), cyclophosphamide (CTX), mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), tacrolimus (TAC), leflunomide (LEF), cyclosporine A and rituximab (RTX). Evaluation of the effectiveness revealed that MMF + GC produced significantly higher overall responses (i.e. complete remission plus partial remission) and that MMF + GC (OR=2.58; 95% CI, 1.67-3.97), CTX + RTX + GC (OR=3.89; 95% CI, 1.60-9.45), CTX + LEF + GC (OR=3.05; 95% CI, 1.05-8.84) and CTX + TAC + GC (OR=6.22; 95% CI, 1.93-20.05) had significantly higher overall responses compared with those to the traditional treatment regimen (CTX + GC). Ranking probability based on the surface under the cumulative ranking curve indicated that CTX + TAC + GC had the highest probability (80.6%) of being the best treatment for achieving an overall response. In the safety evaluation, MMF + GC had a lower risk of infection than CTX + GC (OR=0.32; 95% CI, 0.11,0.88). There were no statistically significant differences in adverse reactions, including gastrointestinal reactions and leukopenia between any two treatment regimens. In conclusion, the regimen of CTX + TAC + GC exhibited a trend in superiority regarding clinical efficacy among common therapeutic drug treatments for RLN, while the regimen of CTX + GC had a higher probability to cause adverse effects among the nine interventions compared.
Keywords: cyclophosphamide; mycophenolate mofetil; network meta-analysis; refractory lupus nephritis; tacrolimus.
Copyright: © Zhou et al.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of 12 immunosuppressive agents for idiopathic membranous nephropathy in adults: A pairwise and network meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 25;13:917532. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.917532. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35959430 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of treatment response and serious infection using tacrolimus, tacrolimus with mycophenolate mofetil, in comparison to cyclophosphamide as induction treatment for lupus nephritis.Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Oct;58(10):550-556. doi: 10.5414/CP203736. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32691727
-
Efficacy and safety of cyclophosphamide combined with mycophenolate mofetil for induction treatment of class IV lupus nephritis.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Nov 15;8(11):21572-8. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26885107 Free PMC article.
-
Rituximab, tacrolimus, cyclophosphamide and cyclosporin in primary membranous nephropathy with nephrotic syndrome: comparison of safety profiles, effect on remission rate, 24-h urinary total protein, serum albumin, and serum creatinine levels using network meta-analysis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 May 8. doi: 10.1007/s11255-025-04549-4. Online ahead of print. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40338506
-
Immunosuppressive treatment for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: An updated network meta-analysis.Open Life Sci. 2023 Jan 10;18(1):20220527. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0527. eCollection 2023. Open Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36694696 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Therapeutic effect of mycophenolate mofetil or cyclophosphamide in children with Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis of different age groups].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Nov 15;25(11):1113-1117. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2306085. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37990454 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Biological therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus, antiphospholipid syndrome, and Sjögren's syndrome: evidence- and practice-based guidance.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 17;14:1117699. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1117699. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37138867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association Between Mycophenolate Mofetil Use and Subsequent Infections Among Hospitalized Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Nested Case-Control Study.Rheumatol Ther. 2023 Dec;10(6):1535-1554. doi: 10.1007/s40744-023-00595-5. Epub 2023 Sep 24. Rheumatol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37742321 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide therapy for Henoch schonlein purpura nephritis in children: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jul 26;103(30):e39059. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039059. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39058868 Free PMC article.
-
The role of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) in kidney diseases.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 28;10:1247690. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1247690. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37841018 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Momtaz M, Fayed A, Wadie M, Gamal SM, Ghoniem SA, Sobhy N, Kamal Elden NM, Hamza WM. Retrospective analysis of nephritis response and renal outcome in a cohort of 928 Egyptian lupus nephritis patients: A university hospital experience. Lupus. 2017;26:1564–1570. doi: 10.1177/0961203317716320. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
