The role of long non-coding RNA H19 in breast cancer
- PMID: 31897110
- PMCID: PMC6924119
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.11093
The role of long non-coding RNA H19 in breast cancer
Abstract
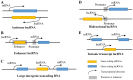
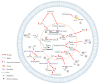
Breast cancer is the most common malignant tumor in women in the majority of countries, such as China, Britain and Australia, and its morbidity and mortality rates remain very high. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) >200 nucleotides in length that lack open reading frames. LncRNA H19 is a transcription product of the H19 gene, and the aberrant expression of H19 can be demonstrated in various types of tumor cell. The purpose of the present review was to elaborate the role of H19 in breast cancer. H19 can regulate gene expression in breast cancer at multiple levels, including epigenetic, transcriptional and posttranscriptional. The abnormal expression of H19 is closely associated with the tumorigenesis and progression of breast cancer via different underlying molecular mechanisms, such as encoding microRNA-675, competing endogenous RNA regulation and interacting with MYC. A large number of clinical studies have suggested that H19 can serve as a potential biomarker for the diagnosis of breast cancer. High expression levels of H19 increases the drug resistance of breast cancer cells and is associated with poor prognosis within patients with breast cancer. Therefore, serum H19 levels may have momentous significance in the clinical setting.
Keywords: H19; biological markers; breast cancer; drug resistance; long non-coding RNA.
Copyright: © Wang et al.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
