Status and prognostic nomogram of patients with Burkitt lymphoma
- PMID: 31897210
- PMCID: PMC6924199
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.11155
Status and prognostic nomogram of patients with Burkitt lymphoma
Abstract
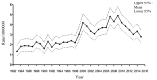
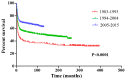
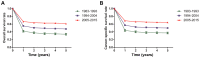
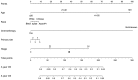
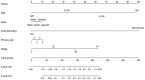
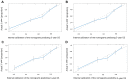
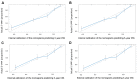
The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the newest status of patients diagnosed Burkitt lymphoma (BL), an aggressive lymphoma subset with a high cure rate. Furthermore, the study aimed to create prognostic nomograms to consider various prognostic factors and estimate patient survival, paving the way for clinical decision-making. A total of 4,600 patients diagnosed with BL between 1983 and 2015 were investigated, via data collected from the SEER database. The overall status of the patients was analyzed through several aspects, including incidence and survival analysis of the previous three decades using the log-rank test and the Kaplan-Meier method. In order to construct and validate the nomograms, the patient diagnosed during 2005-2015 were randomly assigned to the training cohort and validation cohort. Univariate and multivariate analyses were applied to identify independent factors that were further included in the nomograms, predicting 3- and 5-year overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS). The data of the training cohort were used for internal validation and validation cohort used to external validation. C-index and calibration plots were used to validate the nomograms, comparing predicted values with actual outcomes. The incidence of BL was gradually increased from 1984 and reached its peak in 2009, at a rate of 0.491 per 100,000 [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.412-0.581]. From 2009, the incidence slowly declined year by year and dropped to 0.280 per 100,000 (95% CI, 0.224-0.346). The OS and CSS rates of patients diagnosed between 2005 and 2015 were increased, in contrast with those of patients diagnosed from 1983-1993 and 1994-2004. A total of five variables, including age, race, chemotherapy, primary site and stage, proved to be the prognostic factors of BL and were used to construct the nomograms predicting 3- and 5-year OS and CSS. The internal and external calibration plots for the probability of 3- and 5-year OS and CSS were consistent between nomogram prediction and observed outcomes. The slow decline in incidence and the significantly improved cure rate make BL a disease that is no longer an urgent problem. Effective nomograms were developed to predict the OS and CSS of patients with BL.
Keywords: Burkitt lymphoma; incidence; nomogram; prediction model; survival analysis.
Copyright: © Lu et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nomograms for predicting the overall and cancer-specific survival of patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma: a SEER-based study.Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 9;8(54):92978-92988. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21722. eCollection 2017 Nov 3. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29190971 Free PMC article.
-
Nomograms and risk classification systems predicting overall and cancer-specific survival in primary malignant cardiac tumor.J Card Surg. 2019 Dec;34(12):1540-1549. doi: 10.1111/jocs.14299. Epub 2019 Nov 5. J Card Surg. 2019. PMID: 31794125
-
Development and Validation of Nomograms Predicting Overall and Cancer-Specific Survival of Spinal Chondrosarcoma Patients.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018 Nov 1;43(21):E1281-E1289. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000002688. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018. PMID: 29664813
-
Development and Validation of Survival Nomograms in Patients with Primary Bladder Lymphoma.J Clin Med. 2022 Jun 2;11(11):3188. doi: 10.3390/jcm11113188. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35683570 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a prognostic model to predict the prognosis of patients with colorectal gastrointestinal stromal tumor: A large international population-based cohort study.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 2;12:1004662. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1004662. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36408151 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Development of a nomogram to predict the risk of secondary failure of platelet recovery in patients with β-thalassemia major after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a retrospective study.Ther Adv Hematol. 2024 May 9;15:20406207241245190. doi: 10.1177/20406207241245190. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38737005 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase inhibitor induces apoptosis on Epstein-Barr virus positive B lymphoma cells.Anat Cell Biol. 2020 Dec 31;53(4):471-480. doi: 10.5115/acb.20.277. Anat Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 33361545 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term outcomes in patients with Burkitt lymphoma older than 65 years: an analysis of the Texas Cancer Registry.Ann Hematol. 2023 Oct;102(10):2753-2763. doi: 10.1007/s00277-023-05328-w. Epub 2023 Jul 8. Ann Hematol. 2023. PMID: 37422592
-
Development and External Validation of a Nomogram to Predict Cancer-Specific Survival in Patients with Primary Intestinal Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Dec 20;13:9271-9285. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S339907. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34992453 Free PMC article.
-
Hub genes and their key effects on prognosis of Burkitt lymphoma.World J Clin Oncol. 2023 Oct 24;14(10):357-372. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v14.i10.357. World J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37970111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bellan C, Lazzi S, Hummel M, Palummo N, de Santi M, Amato T, Nyagol J, Sabattini E, Lazure T, Pileri SA, et al. Immunoglobulin gene analysis reveals 2 distinct cells of origin for EBV-positive and EBV-negative Burkitt lymphomas. Blood. 2005;106:1031–1036. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-01-0168. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
