The structure-activity relationship review of the main bioactive constituents of Morus genus plants
- PMID: 31897975
- PMCID: PMC7205851
- DOI: 10.1007/s11418-019-01383-8
The structure-activity relationship review of the main bioactive constituents of Morus genus plants
Erratum in
-
Correction to: The structure-activity relationship review of the main bioactive constituents of Morus genus plants.J Nat Med. 2020 Jun;74(3):617. doi: 10.1007/s11418-020-01406-9. J Nat Med. 2020. PMID: 32274685 Free PMC article.
Abstract
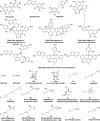
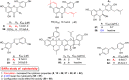
Morus genus plants are mainly distributed in the temperate to tropical areas over the world and include 17 species and two subspecies. Due to their excellent pharmacological activity, security in food additives and high value in the national economy, Morus genus plants have drawn more and more attention in recent years. In the light of the references published over the last few decades, flavonoids, benzofurans, stilbenes, and Diels-Alder adducts have been reported to be the main bioactive constituents of Morus genus plants. This review summarizes the compounds with excellent bioactivities isolated from Morus genus plants as well as their structure-activity relationships (SARs), which might be useful for the further research and development of Morus genus plants. The aromatic heterocycles with excellent bioactivities isolated from Morus genus plants as well as their structure-activity relationships (SARs) were summarized.
Keywords: Bioactive constituents; Morus genus plants; Structure–activity relationships.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Natural Products and Biological Activities of Plants from Genus Morus: 2011-2023.Curr Top Med Chem. 2023;23(28):2640-2698. doi: 10.2174/0115680266257370230920055003. Curr Top Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37818581 Review.
-
The latest review on the polyphenols and their bioactivities of Chinese Morus plants.J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2014;16(6):690-702. doi: 10.1080/10286020.2014.923405. Epub 2014 Jun 9. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2014. PMID: 24911924 Review.
-
Structures, activities, and putative biosynthetic pathways of characteristic polyphenolic compounds from Morus plants: A review.Fitoterapia. 2024 Oct;178:106181. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2024.106181. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Fitoterapia. 2024. PMID: 39154853 Review.
-
Diels-Alder adducts with PTP1B inhibition from Morus notabilis.Phytochemistry. 2015 Jan;109:140-6. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.10.015. Epub 2014 Nov 7. Phytochemistry. 2015. PMID: 25457492
-
Synthesis, Biosynthesis, and Biological Activity of Diels-Alder Adducts from Morus Genus: An Update.Molecules. 2022 Nov 4;27(21):7580. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217580. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364405 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mulberry Diels-Alder-type adducts: isolation, structure, bioactivity, and synthesis.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2022 Sep 2;12(1):31. doi: 10.1007/s13659-022-00355-y. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2022. PMID: 36050566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
White Mulberry Plant Extracts in Cardiovascular Prevention: An Update.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 9;17(14):2262. doi: 10.3390/nu17142262. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40732887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosynthesis and Pharmacological Activities of the Bioactive Compounds of White Mulberry (Morus alba): Current Paradigms and Future Challenges.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jul 7;13(7):506. doi: 10.3390/biology13070506. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical and Biological Review of Endophytic Fungi Associated with Morus sp. (Moraceae) and In Silico Study of Their Antidiabetic Potential.Molecules. 2023 Feb 10;28(4):1718. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041718. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytochemical Composition of Different Botanical Parts of Morus Species, Health Benefits and Application in Food Industry.Plants (Basel). 2022 Jan 6;11(2):152. doi: 10.3390/plants11020152. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35050040 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chan EW, Lye PY, Wong SK. Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and clinical trials of Morus alba. Chin J Nat Med. 2016;14(1):17–30. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

