MicroRNAs in tumor immunity: functional regulation in tumor-associated macrophages
- PMID: 31898439
- PMCID: PMC6964996
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B1900452
MicroRNAs in tumor immunity: functional regulation in tumor-associated macrophages
Abstract
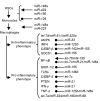
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are the most abundant immune cells in the tumor microenvironment (TME) and are critical for cancer initiation and progression. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) could notably influence the phenotype of TAMs through various targets and signal pathways during cancer progression due to their post-transcriptional regulation. In this review, we discuss mainly the regulatory function of miRNAs on macrophage differentiation, functional polarization, and cellular crosstalk. Firstly, during the generation process, miRNAs take part in the differentiation from myeloid cells to mature macrophages, and this maturation process directly influences their recruitment into the TME, attracted by tumor cells. Secondly, macrophages in the TME can be either tumor-promoting or tumor-suppressing, depending on their functional polarization. Large numbers of miRNAs can influence the polarization of macrophages, which is crucial for tumor progression, including tumor cell invasion, intravasation, extravasation, and premetastatic site formation. Thirdly, crosstalk between tumor cells and macrophages is essential for TME formation and tumor progression, and miRNAs can be the mediator of communication in different forms, especially when encapsulated in microvesicles or exosomes. We also assess the potential value of certain macrophage-related miRNAs (MRMs) as diagnostic and prognostic markers, and discuss the possible development of MRM-based therapies.
Keywords: MicroRNA; Tumor microenvironment; Tumor-associated macrophage; Functional polarization.
Conflict of interest statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

