Epigenetics of colorectal cancer: biomarker and therapeutic potential
- PMID: 31900466
- PMCID: PMC7228650
- DOI: 10.1038/s41575-019-0230-y
Epigenetics of colorectal cancer: biomarker and therapeutic potential
Abstract
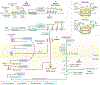
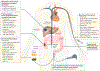
Colorectal cancer (CRC), a leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide, evolves as a result of the stepwise accumulation of a series of genetic and epigenetic alterations in the normal colonic epithelium, leading to the development of colorectal adenomas and invasive adenocarcinomas. Although genetic alterations have a major role in a subset of CRCs, the pathophysiological contribution of epigenetic aberrations in this malignancy has attracted considerable attention. Data from the past couple of decades has unequivocally illustrated that epigenetic marks are important molecular hallmarks of cancer, as they occur very early in disease pathogenesis, involve virtually all key cancer-associated pathways and, most importantly, can be exploited as clinically relevant disease biomarkers for diagnosis, prognostication and prediction of treatment response. In this Review, we summarize the current knowledge on the best-studied epigenetic modifications in CRC, including DNA methylation and histone modifications, as well as the role of non-coding RNAs as epigenetic regulators. We focus on the emerging potential for the bench-to-bedside translation of some of these epigenetic alterations into clinical practice and discuss the burgeoning evidence supporting the potential of emerging epigenetic therapies in CRC as we usher in the era of precision medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
F.B. declares that he has endoscopic equipment on loan from Fujifilm, and has received an honorarium for consultancy from Sysmex and speaker’s fees from Norgine. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bray F et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin 68, 394–424 (2018). - PubMed
-
- ECIS - European Cancer Information System From https://ecis.jrc.ec.europa.eu, accessed on 13/08/2019.
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD & Jemal A Cancer statistics of American 2019. CA. Cancer J. Clin 69, 7–34 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Dienstmann R et al. Consensus molecular subtypes and the evolution of precision medicine in colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 17, 79–92 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

