Clinical value of renal phospholipase A2 receptor deposit in the prognosis evaluation and treatment options of idiopathic membranous nephropathy: A retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 31900967
- PMCID: PMC7065056
- DOI: 10.1111/nep.13691
Clinical value of renal phospholipase A2 receptor deposit in the prognosis evaluation and treatment options of idiopathic membranous nephropathy: A retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Aim: Phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) is a target antigen for idiopathic membranous nephropathy (IMN). However, the association between renal PLA2R antigen and disease prognosis had not been fully investigated. In addition, there was a paucity of studies investigating the difference of therapeutic effects between cyclophosphamide and cyclosporine A in PLA2R-associated IMN.
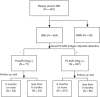
Methods: This retrospective cohort study recruited 300 eligible patients diagnosed with biopsy-proven IMN between September 2015 and July 2018 in Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital. The remission of proteinuria was compared between PLA2R-associated and non-PLA2R-associated IMN. The difference of therapeutic effects between cyclophosphamide and cyclosporine A were also investigated in PLA2R-associated IMN.
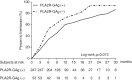
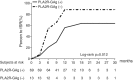
Results: The positive rate of renal PLA2R antigen in recruited IMN patients was 82.3%. Non-PLA2R-associated IMN patients had a higher probability to achieve remission than PLA2R-associated IMN patients (Log-rank test, P = .013). Multivariate COX analysis showed that renal PLA2R antigen was an independent risk factor for not achieving remission in IMN patients (Hazard Ratio: 1.619; 95% confidence interval: 1.133 to 2.313; P = .008). In PLA2R-associated IMN, patients receiving cyclophosphamide had a higher probability to achieve remission compared with those receiving cyclosporine A (Log-rank test, P = .018) while there was no difference in renal survival. Multivariate COX regression analysis showed that compared with cyclosporine A, patients receiving cyclophosphamide had a higher probability to achieve remission.
Conclusion: Phospholipase A2 receptor -associated IMN patients had a lower probability to achieve remission compared with non-PLA2R-associated IMN. Compared with cyclosporine A, cyclophosphamide exerted better therapeutic effects in remission of proteinuria and may be the preferred immunosuppressant for PLA2R-associated IMN. SUMMARY AT A GLANCE This article highlighted the prognostic value of intra-renal phospholipase A2 receptor deposition in idiopathic membranous nephropathy (IMN). Renal phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R)-associated IMN patients had a lower probability to achieve remission compared with non-PLA2R-associated IMN.
Keywords: idiopathic membranous nephropathy; phospholipase A2 receptor; prognosis evaluation; treatment options.
© 2020 Asian Pacific Society of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinical and Histological Features of Phospholipase A2 Receptor-Associated and Thrombospondin Type-I Domain-containing 7A-Associated Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy: A Single Center Retrospective Study from China.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Jul 22;24:5076-5083. doi: 10.12659/MSM.909815. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30032157 Free PMC article.
-
Response to immunosuppressive therapy in PLA2R- associated and non-PLA2R- associated idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a retrospective, multicenter cohort study.BMC Nephrol. 2017 Jul 10;18(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s12882-017-0636-0. BMC Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28693446 Free PMC article.
-
Renal Phospholipase A2 Receptor and the Clinical Features of Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy.Chin Med J (Engl). 2017 Apr 20;130(8):892-898. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.204096. Chin Med J (Engl). 2017. PMID: 28397717 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical usefulness of autoantibodies to M-type phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) for monitoring disease activity in idiopathic membranous nephropathy (IMN).Autoimmun Rev. 2016 Feb;15(2):146-54. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2015.10.004. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Autoimmun Rev. 2016. PMID: 26527329 Review.
-
Phospholipase A2 Receptor Antibodies and Clinical Prognosis in Patients with Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Kidney Blood Press Res. 2023;48(1):102-113. doi: 10.1159/000529415. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2023. PMID: 36720217
Cited by
-
Combined evaluation of glomerular phospholipase A2 receptor and immunoglobulin G subclass in membranous nephropathy.Clin Kidney J. 2024 Apr 17;17(6):sfae104. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfae104. eCollection 2024 Jun. Clin Kidney J. 2024. PMID: 38854426 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction model for treatment response of primary membranous nephropathy with nephrotic syndrome.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2024 Aug;28(8):740-750. doi: 10.1007/s10157-024-02470-1. Epub 2024 May 6. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38709377
-
Renal tubulointerstitial lesions: a prognostic marker in idiopathic membranous nephropathy.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2501379. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2501379. Epub 2025 May 22. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40404172 Free PMC article.
-
Association of M-Type Phospholipase A2 Receptor Deposition in Kidney Tissue with Treatment Outcomes in Patients with Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Dec 22;16:6319-6328. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S427045. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 38149114 Free PMC article.
-
THSD7A as a Promising Biomarker for Membranous Nephrosis.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Nov;66(11):3117-3135. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00934-5. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37884765 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

