Combining molecular and imaging metrics in cancer: radiogenomics
- PMID: 31901171
- PMCID: PMC6942081
- DOI: 10.1186/s13244-019-0795-6
Combining molecular and imaging metrics in cancer: radiogenomics
Abstract
Background: Radiogenomics is the extension of radiomics through the combination of genetic and radiomic data. Because genetic testing remains expensive, invasive, and time-consuming, and thus unavailable for all patients, radiogenomics may play an important role in providing accurate imaging surrogates which are correlated with genetic expression, thereby serving as a substitute for genetic testing.
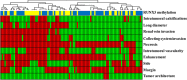
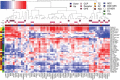
Main body: In this article, we define the meaning of radiogenomics and the difference between radiomics and radiogenomics. We provide an up-to-date review of the radiomics and radiogenomics literature in oncology, focusing on breast, brain, gynecological, liver, kidney, prostate and lung malignancies. We also discuss the current challenges to radiogenomics analysis.
Conclusion: Radiomics and radiogenomics are promising to increase precision in diagnosis, assessment of prognosis, and prediction of treatment response, providing valuable information for patient care throughout the course of the disease, given that this information is easily obtainable with imaging. Larger prospective studies and standardization will be needed to define relevant imaging biomarkers before they can be implemented into the clinical workflow.
Keywords: Molecular profiling; Precision medicine; Radiogenomics; Radiomics.
Conflict of interest statement
Katja Pinker received payment for activities not related to the present article including lectures including service on speakers bureaus and for travel/accommodations/meeting expenses unrelated to activities listed from the European Society of Breast Imaging (MRI educational course, annual scientific meeting) and the IDKD 2019 (educational course). Elizabeth A Morris has received a grant from GRAIL Inc. The rest of the authors declare no potential competing interests.
Figures