Lipid Droplet-Derived Monounsaturated Fatty Acids Traffic via PLIN5 to Allosterically Activate SIRT1
- PMID: 31901447
- PMCID: PMC7036014
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.12.003
Lipid Droplet-Derived Monounsaturated Fatty Acids Traffic via PLIN5 to Allosterically Activate SIRT1
Abstract
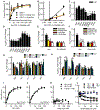
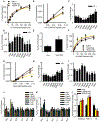
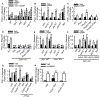
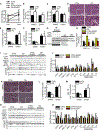
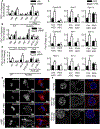
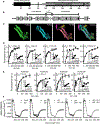
Lipid droplets (LDs) provide a reservoir for triacylglycerol storage and are a central hub for fatty acid trafficking and signaling in cells. Lipolysis promotes mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative metabolism via a SIRT1/PGC-1α/PPARα-dependent pathway through an unknown mechanism. Herein, we identify that monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) allosterically activate SIRT1 toward select peptide-substrates such as PGC-1α. MUFAs enhance PGC-1α/PPARα signaling and promote oxidative metabolism in cells and animal models in a SIRT1-dependent manner. Moreover, we characterize the LD protein perilipin 5 (PLIN5), which is known to enhance mitochondrial biogenesis and function, to be a fatty-acid-binding protein that preferentially binds LD-derived monounsaturated fatty acids and traffics them to the nucleus following cAMP/PKA-mediated lipolytic stimulation. Thus, these studies identify the first-known endogenous allosteric modulators of SIRT1 and characterize a LD-nuclear signaling axis that underlies the known metabolic benefits of MUFAs and PLIN5.
Keywords: ATGL; MUFA; PGC-1α; PLIN5; SIRT1; fatty acids; lipid droplets; lipolysis; olive oil; oxidative metabolism.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Atshaves BP, Petrescu AD, Starodub O, Roths JB, Kier AB, and Schroeder F (1999). Expression and intracellular processing of the 58 KDa SCP-x/3-oxoacyl-CoA thiolase in transfected mouse L cells. J Lipid Res 40, 610–622. - PubMed
-
- Atshaves BP, Storey SM, Petrescu AD, Greenberg C, Lyuksyutova OI, Smith R III, and Schroeder F (2002). Expression of Fatty Acid Binding Proteins Inhibits Lipid Accumulation and Alters Toxicity in L-cell Fibroblasts. Am J Phys 283, C688–C703. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K99 AG070104/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK114401/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053189/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA182543/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG029796/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG055452/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- L30 DK110338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007203/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098203/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK109556/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK083250/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK108790/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

