Targeted protein degradation: current and future challenges
- PMID: 31901786
- PMCID: PMC7615046
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2019.11.012
Targeted protein degradation: current and future challenges
Abstract
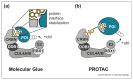
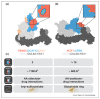
Traditional approaches in the development of small-molecule drugs typically aim to inhibit the biochemical activity of functional protein domains. In contrast, targeted protein degradation aims to reduce overall levels of disease-relevant proteins. Mechanistically, this can be achieved via chemical ligands that induce molecular proximity between an E3 ubiquitin ligase and a protein of interest, leading to ubiquitination and degradation of the protein of interest. This paradigm-shifting pharmacology promises to address several limitations inherent to conventional inhibitor design. Most notably, targeted protein degradation has the potential not only to expand the druggable proteome beyond the reach of traditional competitive inhibitors but also to develop therapeutic strategies of unmatched selectivity. This review briefly summarizes key challenges that remain to be addressed to deliver on these promises and to realize the full therapeutic potential of pharmacologic modulation of protein degradation pathways.
Keywords: Chemical biology; E3 ligase; Molecular glues; PROTACs; Targeted protein degradation.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Nothing declared.
Figures
References
-
- Liu J, Farmer JD, Lane WS, Friedman J, Weissman I, Schreiber SL. Calcineurin is a common target of cyclophilin-cyclosporin A and FKBP-FK506 complexes. Cell. 1991;66:807–815. - PubMed
-
- Griffith JP, Kim JL, Kim EE, Sintchak MD, Thomson JA, Fitzgibbon MJ, Fleming MA, Caron PR, Hsiao K, Navia MA. X-ray structure of calcineurin inhibited by the immunophilin-immunosuppressant FKBP12-FK506 complex. Cell. 1995;82:507–522. - PubMed
-
- Stan R, McLaughlin MM, Cafferkey R, Johnson RK, Rosenberg M, Livi GP. Interaction between FKBP12-rapamycin and TOR involves a conserved serine residue. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:32027–32030. - PubMed
-
- Tan X, Calderon-Villalobos LIA, Sharon M, Zheng C, Robinson CV, Estelle M, Zheng N. Mechanism of auxin perception by the TIR1 ubiquitin ligase. Nature. 2007;446:640–645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

