The role of lipocalin-2 in age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
- PMID: 31901947
- PMCID: PMC7079812
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-019-03423-8
The role of lipocalin-2 in age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
Abstract
Lipocalins are a family of secreted adipokines which play important roles in various biological processes. Lipocalin-2 (LCN-2) has been shown to be involved in acute and chronic inflammation. This particular protein is critical in the pathogenesis of several diseases including cancer, diabetes, obesity, and multiple sclerosis. Herein, we discuss the general molecular basis for the involvement of LCN-2 in acute infections and chronic disease progression and also ascertain the probable role of LCN-2 in ocular diseases, particularly in age-related macular degeneration (AMD). We elaborate on the signaling cascades which trigger LCN-2 upregulation in AMD and suggest therapeutic strategies for targeting such pathways.
Keywords: AKT2 signaling; Age-related macular degeneration (AMD); Inflammation; Lipocalin-2 (LCN-2); Retinal degeneration.
Figures

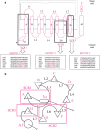
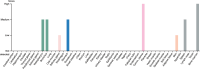

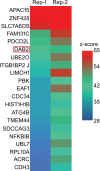


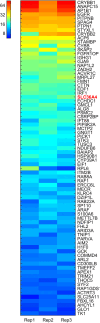





References
-
- Flower DR. The lipocalin protein family: a role in cell regulation. FEBS Lett. 1994;354:7–11. - PubMed
-
- Flower DR, North AC, Sansom CE. The lipocalin protein family: structural and sequence overview. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1482:9–24. - PubMed
-
- Ganfornina MD, Gutierrez G, Bastiani M, Sanchez D. A phylogenetic analysis of the lipocalin protein family. Mol Biol Evol. 2000;17:114–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

