Caregiver involvement in interventions for improving children's dietary intake and physical activity behaviors
- PMID: 31902132
- PMCID: PMC6956675
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012547.pub2
Caregiver involvement in interventions for improving children's dietary intake and physical activity behaviors
Abstract
Background: Poor diet and insufficient physical activity are major risk factors for non-communicable diseases. Developing healthy diet and physical activity behaviors early in life is important as these behaviors track between childhood and adulthood. Parents and other adult caregivers have important influences on children's health behaviors, but whether their involvement in children's nutrition and physical activity interventions contributes to intervention effectiveness is not known.
Objectives: • To assess effects of caregiver involvement in interventions for improving children's dietary intake and physical activity behaviors, including those intended to prevent overweight and obesity • To describe intervention content and behavior change techniques employed, drawing from a behavior change technique taxonomy developed and advanced by Abraham, Michie, and colleagues (Abraham 2008; Michie 2011; Michie 2013; Michie 2015) • To identify content and techniques related to reported outcomes when such information was reported in included studies SEARCH METHODS: In January 2019, we searched CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, 11 other databases, and three trials registers. We also searched the references lists of relevant reports and systematic reviews.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and quasi-RCTs evaluating the effects of interventions to improve children's dietary intake or physical activity behavior, or both, with children aged 2 to 18 years as active participants and at least one component involving caregivers versus the same interventions but without the caregiver component(s). We excluded interventions meant as treatment or targeting children with pre-existing conditions, as well as caregiver-child units residing in orphanages and school hostel environments.
Data collection and analysis: We used standard methodological procedures outlined by Cochrane.
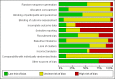
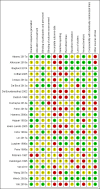
Main results: We included 23 trials with approximately 12,192 children in eligible intervention arms. With the exception of two studies, all were conducted in high-income countries, with more than half performed in North America. Most studies were school-based and involved the addition of healthy eating or physical education classes, or both, sometimes in tandem with other changes to the school environment. The specific intervention strategies used were not always reported completely. However, based on available reports, the behavior change techniques used most commonly in the child-only arm were "shaping knowledge," "comparison of behavior," "feedback and monitoring," and "repetition and substitution." In the child + caregiver arm, the strategies used most commonly included additional "shaping knowledge" or "feedback and monitoring" techniques, as well as "social support" and "natural consequences." We considered all trials to be at high risk of bias for at least one design factor. Seven trials did not contribute any data to analyses. The quality of reporting of intervention content varied between studies, and there was limited scope for meta-analysis. Both validated and non-validated instruments were used to measure outcomes of interest. Outcomes measured and reported differed between studies, with 16 studies contributing data to the meta-analyses. About three-quarters of studies reported their funding sources; no studies reported industry funding. We assessed the quality of evidence to be low or very low. Dietary behavior change interventions with a caregiver component versus interventions without a caregiver component Seven studies compared dietary behavior change interventions with and without a caregiver component. At the end of the intervention, we did not detect a difference between intervention arms in children's percentage of total energy intake from saturated fat (mean difference [MD] -0.42%, 95% confidence interval [CI] -1.25 to 0.41, 1 study, n = 207; low-quality evidence) or from sodium intake (MD -0.12 g/d, 95% CI -0.36 to 0.12, 1 study, n = 207; low-quality evidence). No trial in this comparison reported data for children's combined fruit and vegetable intake, sugar-sweetened beverage (SSB) intake, or physical activity levels, nor for adverse effects of interventions. Physical activity interventions with a caregiver component versus interventions without a caregiver component Six studies compared physical activity interventions with and without a caregiver component. At the end of the intervention, we did not detect a difference between intervention arms in children's total physical activity (MD 0.20 min/h, 95% CI -1.19 to 1.59, 1 study, n = 54; low-quality evidence) or moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA) (standard mean difference [SMD] 0.04, 95% CI -0.41 to 0.49, 2 studies, n = 80; moderate-quality evidence). No trial in this comparison reported data for percentage of children's total energy intake from saturated fat, sodium intake, fruit and vegetable intake, or SSB intake, nor for adverse effects of interventions. Combined dietary and physical activity interventions with a caregiver component versus interventions without a caregiver component Ten studies compared dietary and physical activity interventions with and without a caregiver component. At the end of the intervention, we detected a small positive impact of a caregiver component on children's SSB intake (SMD -0.28, 95% CI -0.44 to -0.12, 3 studies, n = 651; moderate-quality evidence). We did not detect a difference between intervention arms in children's percentage of total energy intake from saturated fat (MD 0.06%, 95% CI -0.67 to 0.80, 2 studies, n = 216; very low-quality evidence), sodium intake (MD 35.94 mg/d, 95% CI -322.60 to 394.47, 2 studies, n = 315; very low-quality evidence), fruit and vegetable intake (MD 0.38 servings/d, 95% CI -0.51 to 1.27, 1 study, n = 134; very low-quality evidence), total physical activity (MD 1.81 min/d, 95% CI -15.18 to 18.80, 2 studies, n = 573; low-quality evidence), or MVPA (MD -0.05 min/d, 95% CI -18.57 to 18.47, 1 study, n = 622; very low-quality evidence). One trial indicated that no adverse events were reported by study participants but did not provide data.
Authors' conclusions: Current evidence is insufficient to support the inclusion of caregiver involvement in interventions to improve children's dietary intake or physical activity behavior, or both. For most outcomes, the quality of the evidence is adversely impacted by the small number of studies with available data, limited effective sample sizes, risk of bias, and imprecision. To establish the value of caregiver involvement, additional studies measuring clinically important outcomes using valid and reliable measures, employing appropriate design and power, and following established reporting guidelines are needed, as is evidence on how such interventions might contribute to health equity.
Copyright © 2020 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Emily H Morgan (EHM) received funding from Cornell University to attend the World Health Organization (WHO)/Cochrane/Cornell University Summer Institute for Systematic Reviews in Nutrition for Global Policy Making, hosted by the Division of Nutritional Sciences, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York, USA, July 27 to August 7, 2015. Additionally, EHM was partially supported by a Fellowship from Cochrane South Africa, South African Medical Research Council, which is funded by the Effective Health Care Research Consortium. This Consortium is funded by UK aid from the UK Government for the benefit of developing countries (Grant 5242). This Fellowship financed EHM's travel to Stellenbosch University for two weeks in 2018 to facilitate collaboration. Additionally, EHM declares that she is part owner of a small business that sells hearing aids. EHM does not believe this poses any conflict but declares it as an interest in the medical/health field.
Anel Schoonees (AS) received a Developing Country Stipend in 2018 from Cochrane to attend the Cochrane Colloquium in Edinburgh, UK. This was not related to this review, but AS declares it in the interest of transparency.
Urshila Sriram—none known.
Marlyn Faure—none known.
Rebecca A Seguin—none known.
Disclaimer: the views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect UK government policy.
Figures



Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Adamo 2017a {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Adamo K. Queries re: Activity Begins in Childhood [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, July 19, 2019.
-
- Adamo KB, Barrowman N, Naylor PJ, Yaya S, Harvey A, Grattan KP, et al. Activity Begins in Childhood (ABC)—inspiring healthy active behaviour in preschoolers: study protocol for a cluster randomized controlled trial. Trials 2014;15:305. [DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-15-305; PMC4124151; PUBMED: 25073797] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- ISRCTN94022291. Activity begins in childhood—a study to inspire healthy active behaviour in preschoolers [Activity begins in childhood—a randomized controlled trial to inspire healthy active behaviour in preschoolers]. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN94022291 (first received December 11, 2012). [DOI: 10.1186/ISRCTN94022291] - DOI
Alhassan 2018a {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Alhassan S, Nwaokelemeh O, Greever CJ, Burkart S, Ahmadi M, Laurent CW, et al. Effect of a culturally‐tailored mother‐daughter physical activity intervention on pre‐adolescent African‐American girls' physical activity levels. Preventive Medicine Reports 2018;11:7‐14. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2018.05.009; PMC6066471 ; PUBMED: 30065909] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- NCT01588379. Mothers and girls dancing together trial (MAGNET) [Effects of an Afro‐centric dance program for African‐American daughters and mothers]. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01588379 (first received April 25, 2012).
Baghurst 2014 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Baghurst T, Eichmann K. Effectiveness of a child‐only and a child‐plus‐parent nutritional education program. International Journal of Child and Adolescent Health 2014;7(3):229‐37.
Cottrell 2005 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Crespo 2012a {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Ayala GX, Elder, JP, Campbell NR, Arredondo E, Baquero B, Crespo NC, et al. Longitudinal intervention effects on parenting of the Aventuras para Niños study. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2010;38(2):154‐62. [DOI: 10.1016/j.amepre.2009.09.038; PMC2832210; PUBMED: 20117571] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Crespo NC, Elder JP, Ayala GX, Slymen DJ, Campbell NR, Sallis JF, et al. Results of a multi‐level intervention to prevent and control childhood obesity among Latino children: the Aventuras Para Niños Study. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 2012;43(1):84‐100. [DOI: 10.1007/s12160-011-9332-7; PMC4131843; PUBMED: 22215470] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Elder J. Queries re: Aventuras Para Niños [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, October 25, 2018.
-
- Elder JP, Arredondo EM, Campbell N, Baquero B, Duerksen S, Ayala G, et al. Individual, family, and community environmental correlates of obesity in Latino elementary school children. Journal of School Health 2010;80(1):20‐30. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1746-1561.2009.00462.x; PMC4477683; PUBMED: 20051087] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
De Bock 2013a {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- NCT00987532. A participatory parental intervention promoting physical activity in preschools. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00987532 (first received September 30, 2009).
De Bourdeaudhuij 2002 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Bourdeaudhuij I, Brug J, Vandelanotte C, Oost P. Differences in impact between a family‐ versus an individual‐based tailored intervention to reduce fat intake. Health Education Research 2002;17(4):435‐49. [PUBMED: 12197589] - PubMed
Dietsch 1990 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Dietsch BJ. Effectiveness of a School/Community‐based Health Promotion Program on Changes in Diet and Diet‐related Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease: Family Determinants of Change in Adolescents and Their Parents [PhD dissertation]. Los Angeles, CA: University of Southern California, 1990.
Ducheyne 2014a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Cardon G. Queries re: cycle training RCT [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, May 30, 2018.
Frenn 2013a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Frenn M. Follow‐up re: Project FUN [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, June 25, 2018.
Haerens 2006a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Haerens L. Data [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, February 26, 2019.
-
- Haerens L, Bourdeaudhuij I, Maes L, Vereecken C, Brug J, Deforche B. The effects of a middle‐school healthy eating intervention on adolescents' fat and fruit intake and soft drinks consumption. Public Health Nutrition 2007;10(5):443‐9. [DOI: 10.1017/S1368980007219652; PUBMED: 17411463] - DOI - PubMed
Hopper 1992a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Gruber MB. Queries re: completed RCT [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, May 5, 2018.
Ievers Landis 2005 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Ievers‐Landis CE, Burant C, Drotar D, Morgan L, Trapl ES, Colabianchi N, et al. A randomized controlled trial for the primary prevention of osteoporosis among preadolescent girl scouts: 1‐year outcomes of a behavioral program. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 2005;30(2):155‐65. [DOI: 10.1093/jpepsy/jsi003; PUBMED: 15681310] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Landis C. Follow‐up re: RCT with Girl Scouts [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, August 27, 2018.
Kirks 1982a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Fischer BA. Questions about your 1979 study [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, February 27, 2019.
-
- Kirks BA, Hendricks DG, Wyse BW. Parent involvement in nutrition education for primary grade students. Journal of Nutrition Education 1982;14(4):137‐40. [DOI: 10.1016/S0022-3182(82)80156-8] - DOI
-
- Kirks BA, Hughes C. Long‐term behavioral effects of parent involvement in nutrition education. Journal of Nutrition Education 1986;18(5):203‐6. [DOI: 10.1016/S0022-3182(86)80043-7] - DOI
Lin 2017a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Lin CY, Scheerman JFM, Yaseri M, Pakpour AH, Webb TL. A cluster randomized controlled trial of an intervention based on the Health Action Process Approach for increasing fruit and vegetable consumption in Iranian adolescents. Psychology & Health 2017;32(12):1449‐68. [DOI: 10.1080/08870446.2017.1341516; PUBMED: 28681612] - DOI - PubMed
-
- NCT02405611. A multi‐component intervention on improving fruit and vegetable consumption in teenagers and their mothers. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02405611 (first received March 25, 2015).
-
- Pakpour A. Queries about your HAPA intervention for adolescents [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, November 11, 2019.
Luepker 1996a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Feldman H. Catch up [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, December 17, 2018.
-
- Luepker RV, Perry CL, McKinlay SM, Nader PR, Parcel GS, Stone EJ, et al. Outcomes of a field trial to improve children's dietary patterns and physical activity: the Child and Adolescent Trial for Cardiovascular Health (CATCH). JAMA 1996;275(10):768‐76. [DOI: 10.1001/jama.275.10.768; PUBMED: 8598593] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lytle LA, Stone EJ, Nichaman MZ, Perry CL, Montgomery DH, Nicklas TA, et al. Changes in nutrient intakes of elementary school children following a school‐based intervention: results from the CATCH Study. Preventive Medicine 1996;25(4):465‐77. [DOI: 10.1006/pmed.1996.0078; PUBMED: 8818069] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nader PR, Sellers DE, Johnson CC, Perry CL, Stone EJ, Cook KC, et al. The effect of adult participation in a school‐based family intervention to improve children's diet and physical activity: the Child and Adolescent Trial for Cardiovascular Health. Preventive Medicine 1996;25(4):455‐64. [DOI: 10.1006/pmed.1996.0077; PUBMED: 8818068] - DOI - PubMed
Perry 1988a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Luepker R. Queries re: MN Home Team [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, February 28, 2019.
-
- Luepker RV, Perry CL, Murray DM, Mullis R. Hypertension prevention through nutrition education in youth: a school‐based program involving parents. Health Psychology 1988;7 Suppl:233‐45. [PUBMED: 3243221] - PubMed
-
- Perry CL, Luepker RV, Murray DM, Hearn MD, Halper A, Dudovitz B, et al. Parent involvement with children's health promotion: a one‐year follow‐up of the Minnesota home team. Health Education Quarterly 1989;16(2):171‐80. [PUBMED: 2732061] - PubMed
Petchers 1987 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Petchers M. Heart Health [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, May 18, 2018.
-
- Petchers MK, Hirsch EZ, Bloch BA. The impact of parent participation on the effectiveness of a heart health curriculum. Health Education Quarterly 1987;14(4):449‐60. [PUBMED: 3692866] - PubMed
Vandongen 1995 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Burke V, Thompson C, Taggart AC, Spickett EE, Beilin LJ, Vandongen R, et al. Differences in response to nutrition and fitness education programmes in relation to baseline levels of cardiovascular risk in 10 to 12‐year‐old children. Journal of Human Hypertension 1996;10 Suppl 3:S99‐106. [PUBMED: 8872838] - PubMed
-
- Gracey V. Fitness and nutrition trial in children [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, April 17, 2018.
-
- Vandongen R, Jenner DA, Thompson C, Taggart AC, Spickett EE, Burke V, et al. A controlled evaluation of a fitness and nutrition intervention program on cardiovascular health in 10‐ to 12‐year‐old children. Preventive Medicine 1995;24(1):9‐22. [DOI: 10.1006/pmed.1995.1003; PUBMED: 7740021] - DOI - PubMed
Voll 2013 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Voll J. Determining the “Spread of Effects” of Physical Activity Interventions From Children to Parents/Guardians [Masters thesis]. Thunder Bay, ON: Lakeland University, 2012.
Wang 2007a {published data only}
-
- Wang C, Zhao H, Liu P, Ju P, He Z, Cong N. Effect of three ways of nutritional education on knowledge‐attitude‐behavior with nutrition in pupils. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu [Journal of Hygiene Research] 2007;36(1):85‐7. [PUBMED: 17424859] - PubMed
-
- Zhao H. Intervention Study on Improvement of Knowledge, Attitude and Practice With Calcium Nutrition in Pupil [Masters thesis]. Nanjing, JS: Southeast University, 2006.
Werch 2003a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Werch C. New customer message on May 17, 2018 at 02:00 PM [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, May 17, 2018.
-
- Werch C, Moore M, DiClemente CC, Owen DM, Jobli E, Bledsoe R. A sport‐based intervention for preventing alcohol use and promoting physical activity among adolescents. Journal of School Health 2003;73(10):380‐8. [PUBMED: 14727390] - PubMed
Yeh 2018a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Akil N. Evaluation of Effectiveness of Classroom‐based Nutrition Intervention on Changes in Eating Behavior in African American Parents/Caregivers and Their Children [Masters thesis]. Detroit, MI: Wayne State University, 2013.
-
- Yeh Y. Query re: study at Head Start sites in Detroit [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, August 18, 2018.
References to studies excluded from this review
Brannon 2018 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Cushing C. Query on your N‐of‐1 intervention [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, October 9, 2019.
DeVilliers 2009 {published data only}
-
- Villiers A. RE: De Villiers et al 2009 [personal communication]. Email to A Schoonees, March 8, 2018.
-
- Villiers A, Steyn NP, Lambert EV, Fourie J. Preventing diabetes through a primary school‐based intervention—the healthkick program. Journal of Diabetes 2009;1(Suppl 1):A144. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1753-0407.2009.00020.x; onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/j.1753‐0407.2009.00020.x] - DOI
Harrington 2005 {published data only}
-
- Franklin F. Hi5+ study [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, April 28, 2018.
Natale 2016 {published data only}
-
- Natale R. Healthy Caregivers–Healthy Children (HC2): A Childcare Center–based Obesity Prevention Program [personal communication]. Email to A Schoonees, February 15, 2018.
-
- Natale RN, Messiah SE, Chang C, Sardinas K, Fitzgibbons J, Peraza S. Healthy caregivers‐healthy children: a primary prevention program with preschool children. Cardiology 2016;134(Suppl 1):71. [DOI: 10.1159/000447505; Abstract number 059; www.karger.com/Article/Pdf/447505] - DOI
Regev 2012 {published data only}
-
- Regev D, Kedem D, Guttmann J. The effects of mothers' participation in movement therapy on the emotional functioning of their school‐age children in Israel. The Arts in Psychotherapy 2012;39(5):479‐88. [DOI: 10.1016/j.aip.2012.08.003] - DOI
Russell Mayhew 2007 {published data only}
Treu 2017 {published data only}
-
- Njike V. RE: Query re: ASCEND study [personal communication]. Email to A Schoonees, April 30, 2018.
References to studies awaiting assessment
Kobak 2016 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Kobak MS. The Experimental Effect of Parent Versus Peer Influence on Children's Physical Activity Behavior [Doctoral thesis]. Kent, OH: Kent State University College, 2016. [etd.ohiolink.edu/!etd.send_file?accession=kent1459775865&disposition...
NTR5755 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- NTR5755. Strengthening parenting styles and practices in the existing intervention KERNgezond to prevent overweight and obesity in children [Strengthening parenting styles and practices in the existing intervention KERNgezond to prevent overweight and obesity in children, a cluster randomized controlled study]. www.trialregister.nl/trial/5640 (first received February 22, 2016).
Ruiter 2015a {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- NTR3938. Strengthening parenting styles and practices in existing interventions to prevent overweight and obesity in children [Strengthening parenting styles and practices in existing interventions to prevent overweight and obesity in children, a cluster randomized study]. www.trialregister.nl/trial/3752 (first received April 7, 2013).
-
- Ruiter EL, Fransen GA, Molleman GR, Velden K, Engels RC. The effectiveness of a web‐based Dutch parenting program to prevent overweight in children 9‐13 years of age: study protocol for a two‐armed cluster randomized controlled trial. BMC Public Health 2015;15:148. [DOI: 10.1186/s12889-015-1394-1; PMC4335372; PUBMED: 25884190] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Swindle 2017a {published data only}
-
- NCT03075085. Developing and testing implementation strategies for evidence‐based obesity prevention in childcare. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03075085 (first received February 20, 2017).
-
- Swindle T, Johnson SL, Whiteside‐Mansell L, Curran GM. A mixed methods protocol for developing and testing implementation strategies for evidence‐based obesity prevention in childcare: a cluster randomized hybrid type III trial. Implemention Science 2017;12(1):90. [DOI: 10.1186/s13012-017-0624-6; PMC5516351 ; PUBMED: 28720140] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Armstrong 2019a {published data only}
-
- NCT03111264. Building blocks for healthy preschoolers [Building blocks for healthy preschoolers: child care and family models]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03111264 (first received March 27, 2017).
Cunningham Sabo 2016 {published data only}
-
- Cunningham‐Sabo L, Lohse B, Smith S, Browning R, Strutz E, Nigg C, et al. Fuel for fun: a cluster‐randomized controlled study of cooking skills, eating behaviors, and physical activity of 4th graders and their families. BMC Public Health 2016;16:444. [DOI: 10.1186/s12889-016-3118-6; PMC4882848; PUBMED: 27230565] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- NCT02491294. Fuel for fun: cooking with kids plus parents and play (FFF) [Cooking with kids 2.0: plus parents and play]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02491294 (first received July 1, 2015).
Kovalskys 2017a {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- ISRCTN58093412. More jumping and better eating at home and school [MINI SALTEN: study assessing the efficacy of a virtual intervention targeted to parents and aimed at preventing obesity in 6 year old children of public schools of Buenos Aires]. isrctn.com/ISRCTN58093412 (first received March 14, 2016).
-
- Kovalskys I, Indart Rougier P, Luciana L, Rauch Herscovici C, Gregorio MJ. MINI SALTEN: a case study on learnings from Argentina on outcomes and challenges. Annals of Nutrition & Metabolism 2017;71(Suppl 2):96‐7. [DOI: 10.1159/000480486] - DOI
-
- Kovalskys I, Rausch Herscovici C, Indart Rougier P, Gregorio MJ, Zonis L, Orellana L. Study protocol of MINI SALTEN: a technology‐based multi‐component intervention in the school environment targeting healthy habits of first grade children and their parents. BMC Public Health 2017;17(1):401. [DOI: 10.1186/s12889-017-4327-3; PMC5420097 ; PUBMED: 28477624] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
NCT00065247 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Economos C. Query re: BONES [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, October 11, 2019.
-
- NCT00065247. The BONES project: building healthy bones in children [Beat osteoporosis: nourish and exercise skeletons (BONES)]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00065247 (first received July 18, 2003).
NCT02809196 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Frodi Olsen S. NCT02809196, 2014‐01, texts for healthy teens: a health education program for adolescents [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, November 4, 2019.
-
- NCT02809196. Texts for healthy teens: a health education program for adolescents (T4HT) [A digital messaging education program for dietary behavior modification towards healthier lifestyle among Danish adolescents]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02809196 (first received June 20, 2016).
NCT02942823 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Mack I. NCT02942823, KOP_2, Kids Obesity Prevention Program Part 2 [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, October 10, 2019.
-
- NCT02942823. Kids obesity prevention program part 2 (KOP‐2). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02942823 (first received October 19, 2016).
Yin 2019a {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- NCT03590834. Míranos! program, a preschool obesity prevention RCT [Obesity prevention in Head Start: Míranos! program]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03590834 (first received June 27, 2018).
-
- Yin Z. Query re: Miranos! [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, November 3, 2019.
-
- Yin Z, Ullevig SL, Sosa E, Liang Y, Olmstead T, Howard JT, et al. Study protocol for a cluster randomized controlled trial to test "¡Míranos! Look at Us, We Are Healthy!"—an early childhood obesity prevention program. BMC Pediatrics 2019;19(1):190. [DOI: 10.1186/s12887-019-1541-4; PMC6556954 ; PUBMED: 31179916] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Additional references
Abraham 2008
Adamo 2014
-
- Adamo KB, Barrowman N, Naylor PJ, Yaya S, Harvey A, Grattan KP, et al. Activity Begins in Childhood (ABC)—inspiring healthy active behaviour in preschoolers: study protocol for a cluster randomized controlled trial. Trials 2014;15:305. [DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-15-305; PMC4124151; PUBMED: 25073797] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Adamo 2017b
Afshin 2014
-
- Afshin A, Micha R, Khatibzadeh S, Mozaffarian D. Consumption of nuts and legumes and risk of incident ischemic heart disease, stroke, and diabetes: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2014;100(1):278–88. [DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.113.076901; PUBMED: 24898241] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Akil 2013
-
- Akil N. Evaluation of Effectiveness of Classroom‐based Nutrition Intervention on Changes in Eating Behavior in African American Parents/Caregivers and Their Children [Masters thesis]. Detroit, MI: Wayne State University, 2013.
Alhassan 2018
-
- Alhassan S, Nwaokelemeh O, Greever CJ, Burkart S, Ahmadi M, Laurent CW, et al. Effect of a culturally‐tailored mother‐daughter physical activity intervention on pre‐adolescent African‐American girls' physical activity levels. Preventive Medicine Reports 2018;11:7‐14. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2018.05.009; NCT01588379; PMC6066471 ; PUBMED: 30065909] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Armstrong 2019
Ayala 2010
-
- Ayala GX, Elder JP, Campbell NR, Arredondo E, Baquero B, Crespo NC, et al. Longitudinal intervention effects on parenting of the Aventuras para Niños study. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2010;38(2):154‐62. [DOI: 10.1016/j.amepre.2009.09.038; PMC2832210; PUBMED: 20117571] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Barriuso 2015
Bauman 2012
Bautista‐Castaño 2004
-
- Bautista‐Castaño I, Doreste J, Serra‐Majem L. Effectiveness of interventions in the prevention of childhood obesity. European Journal of Epidemiology 2004;19(7):617‐22. [PUBMED: 15461192] - PubMed
Beaglehole 2011
Biswas 2015
-
- Biswas A, Oh PI, Faulkner GE, Bajaj RR, Silver MA, Mitchell MS, et al. Sedentary time and its association with risk for disease incidence, mortality, and hospitalization in adults: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Annals of Internal Medicine 2015;162(2):123‐32. [DOI: 10.7326/M14-1651] - DOI - PubMed
Black 2013
Blissett 2011
Brown 2009
Brown 2019
Burkart 2017
Burke 1996
-
- Burke V, Thompson C, Taggart AC, Spickett EE, Beilin LJ, Vandongen R, et al. Differences in response to nutrition and fitness education programmes in relation to baseline levels of cardiovascular risk in 10 to 12‐year‐old children. Journal of Human Hypertension 1996;10 Suppl 3:S99‐106. [PUBMED: 8872838] - PubMed
Buttitta 2014
Cardon 2018 [pers comm]
-
- Cardon G. Queries re: cycle training RCT [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, May 30, 2018.
Chan 2011
Cheungpasitporn 2014
-
- Cheungpasitporn W, Thongprayoon C, O'Corragain OA, Edmonds PJ, Kittanamongkolchai W, Erickson SB. Associations of sugar‐sweetened and artificially sweetened soda with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Nephrology 2014;19(12):791‐7. [DOI: 10.1111/nep.12343; PUBMED: 25251417] - DOI - PubMed
Chung 2016
Clark 2007
Cole 2000
Covidence [Computer program]
-
- Veritas Health Innovation. Covidence. Version accessed March 18, 2019. Melbourne, AU: Veritas Health Innovation.
Craigie 2011
Crespo 2012b
-
- Crespo NC, Elder JP, Ayala GX, Slymen DJ, Campbell NR, Sallis JF, et al. Results of a multi‐level intervention to prevent and control childhood obesity among Latino children: the Aventuras Para Niños Study. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 2012;43(1):84‐100. [DOI: 10.1007/s12160-011-9332-7; PMC4131843; PUBMED: 22215470] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Crocket 1989
Crockett 1995
-
- Crockett SJ, Sims LS. Environmental influences on children's eating. Journal of Nutrition Education 1995;27(5):235‐49. [DOI: 10.1016/S0022-3182(12)80792-8] - DOI
Cullen 2008
Cunningham‐Sabo 2016
-
- Cunningham‐Sabo L, Lohse B, Smith S, Browning R, Strutz E, Nigg C, et al. Fuel for fun: a cluster‐randomized controlled study of cooking skills, eating behaviors, and physical activity of 4th graders and their families. BMC Public Health 2016;16:444. [DOI: 10.1186/s12889-016-3118-6; NCT02491294; PMC4882848; PUBMED: 27230565] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Daniels 2009
Darmon 2008
-
- Darmon N, Drewnowski A. Does social class predict diet quality?. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2008;87(5):1107‐17. [PUBMED: 18469226] - PubMed
De Bock 2010
De Bock 2013b
De Onis 2010
De Vet 2011
Diep 2015
-
- Diep CS, Hingle M, Chen TA, Dadabhoy HR, Beltran A, Baranowski J, et al. The Automated Self‐Administered 24‐Hour Dietary Recall for Children, 2012 version, for youth aged 9 to 11 years: a validation study. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics 2015;115(10):1591‐8. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jand.2015.02.021; PMC4584168; PUBMED: 25887784] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Dinsa 2012
Draper 2015
Ducheyne 2014b
Elder 2010
-
- Elder JP, Arredondo EM, Campbell N, Baquero B, Duerksen S, Ayala G, et al. Individual, family, and community environmental correlates of obesity in Latino elementary school children. Journal of School Health 2010;80(1):20‐30. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1746-1561.2009.00462.x; PMC4477683; PUBMED: 20051087] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Feldman 2018 [pers comm]
-
- Feldman H. Catch up [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, December 17, 2018.
Fischer 2019 [pers comm]
-
- Fischer BA. Questions about your 1979 study [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, February 27, 2019.
Forouzanfar 2016
-
- Forouzanfar MH, Afshin A, Alexander L, Anderson HR, Bhutta, ZA, Biryukov S, et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016;388(10053):1659‐724. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31679-8; PUBMED: 27733284] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Frenn 2013b
Frenn 2018 [pers comm]
-
- Frenn M. Follow‐up re: Project FUN [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, June 25, 2018.
Gan 2015
GBD 2017 Diet Collaborators 2019
Golan 2004
-
- Golan M, Crow S. Parents are key players in the prevention and treatment of weight‐related problems. Nutrition Reviews 2004;62(1):39‐50. [PUBMED: 14995056] - PubMed
Golley 2011
-
- Golley RK, Hendrie GA, Slater A, Corsini N. Interventions that involve parents to improve children's weight‐related nutrition intake and activity patterns—what nutrition and activity targets and behaviour change techniques are associated with intervention effectiveness?. Obesity Reviews 2011;12(2):114‐30. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2010.00745.x; PUBMED: 20406416] - DOI - PubMed
Gordon‐Larsen 2000
-
- Gordon‐Larsen P, McMurray RG, Popkin BM. Determinants of adolescent physical activity and inactivity patterns. Pediatrics 2000;105(6):e83. [PUBMED: 10835096] - PubMed
Gracey 2018 [pers comm]
-
- Gracey V. Fitness and nutrition trial in children [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, April 17, 2018.
Gruber 2018 [pers comm]
-
- Gruber MB. Queries re: completed RCT [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, May 5, 2018.
Haerens 2006b
Haerens 2006c
Haerens 2007a
-
- Haerens L, Bourdeaudhuij I, Maes L, Vereecken C, Brug J, Deforche B. The effects of a middle‐school healthy eating intervention on adolescents' fat and fruit intake and soft drinks consumption. Public Health Nutrition 2007;10(5):443‐9. [DOI: 10.1017/S1368980007219652; PUBMED: 17411463] - DOI - PubMed
Haerens 2007b
Haerens 2019 [pers comm]
-
- Haerens L. Data [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, February 26, 2019.
Hall 2009
Hallal 2012
He 2009
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011c
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ (editors). Chapter 7: Selecting studies and collecting data. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hingle 2010
Hoffman 2014
Hopper 1992b
Hu 2014
Huang 2014
Imamura 2015
-
- Imamura F, O'Connor L, Ye Z, Mursu J, Hayashino Y, Bhugathiraju SN, et al. Consumption of sugar sweetened beverages, artificially sweetened beverages, and fruit juice and incidence of type 2 diabetes: systematic review, meta‐analysis, and estimation of population attributable fraction. BMJ 2015;351:h3576. [DOI: 10.1136/bmj.h3576; PMC4510779; PUBMED: 26199070] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
ISRCTN58093412
-
- ISRCTN58093412. More jumping and better eating at home and school [MINI SALTEN: study assessing the efficacy of a virtual intervention targeted to parents and aimed at preventing obesity in 6 year old children of public schools of Buenos Aires]. isrctn.com/ISRCTN58093412 (first received March 14, 2016).
ISRCTN94022291
-
- ISRCTN94022291. Activity begins in childhood—a study to inspire healthy active behaviour in preschoolers [Activity begins in childhood—a randomized controlled trial to inspire healthy active behaviour in preschoolers]. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN94022291 (first received December 11, 2012). [DOI: 10.1186/ISRCTN94022291] - DOI
Jeon 2007
Kader 2015
Kirks 1982b
-
- Kirks BA, Hendricks DG Wyse BW. Parent involvement in nutrition education for primary grade students. Journal of Nutrition Education 1982;14(4):137‐40. [DOI: 10.1016/S0022-3182(82)80156-8] - DOI
Kirks 1986
-
- Kirks BA, Hughes C. Long‐term behavioral effects of parent involvement in nutrition education. Journal of Nutrition Education 1986;18(5):203‐6. [DOI: 10.1016/S0022-3182(86)80043-7] - DOI
Kobes 2018
Kovalskys 2017b
-
- Kovalskys I, Indart Rougier P, Luciana L, Rauch Herscovici C, Gregorio MJ. MINI SALTEN: a case study on learnings from Argentina on outcomes and challenges. Annals of Nutrition & Metabolism 2017;71(Suppl 2):96‐7. [DOI: ]
Kovalskys 2017c
-
- Kovalskys I, Rausch Herscovici C, Indart Rougier P, Gregorio MJ, Zonis L, Orellana L. Study protocol of MINI SALTEN: a technology‐based multi‐component intervention in the school environment targeting healthy habits of first grade children and their parents. BMC Public Health 2017;17(1):401. [DOI: 10.1186/s12889-017-4327-3; ISRCTN58093412; PMCID: PMC5420097 ; PUBMED: 28477624] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Kuczmarski 2002
-
- Kuczmarski RJ, Ogden CL, Guo SS, Grummer‐Strawn LM, Flegal KM, Mei Z, et al. 2000 CDC growth charts for the United States: methods and development. Vital and Health Statistics 2002;11(246):1‐190. [PUBMED: 12043359] - PubMed
Lee 2012
-
- Lee IM, Shiroma EJ, Lobelo F, Puska P, Blair SN, Katzmarzyk PT, for the Lancet Physical Activity Series Working Group. Effect of physical inactivity on major non‐communicable diseases worldwide: an analysis of burden of disease and life expectancy. Lancet 2012;380(9838):219–29. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61031-9] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Lefebvre 2008
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews for Interventions. Chichester (UK): John Wiley & Sons, 2008.
Lin 2017
-
- Lin CY, Scheerman JFM, Yaseri M, Pakpour AH, Webb TL. A cluster randomized controlled trial of an intervention based on the Health Action Process Approach for increasing fruit and vegetable consumption in Iranian adolescents. Psychology & Health 2017;32(12):1449‐68. [DOI: 10.1080/08870446.2017.1341516; PUBMED: 28681612] - DOI - PubMed
Lindsay 2006
-
- Lindsay AC, Sussner KM, Kim J, Gortmaker SL. The role of parents in preventing childhood obesity. The Future of Children 2006;16(1):169‐86. [PUBMED: 16532663] - PubMed
Ling 2017
Lobstein 2015
Lorenc 2013
Loveman 2015
Lozano 2012
-
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012;380(9859):2095–128. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Luepker 1988
-
- Luepker RV, Perry CL, Murray DM, Mullis R. Hypertension prevention through nutrition education in youth: a school‐based program involving parents. Health Psychology 1988;7 Suppl:233‐45. [PUBMED: 3243221] - PubMed
Luepker 1996b
-
- Luepker RV, Perry CL, McKinlay SM, Nader PR, Parcel GS, Stone EJ, et al. Outcomes of a field trial to improve children's dietary patterns and physical activity: the Child and Adolescent Trial for Cardiovascular Health (CATCH). JAMA 1996;275(10):768‐76. [DOI: 10.1001/jama.275.10.768; PUBMED: 8598593] - DOI - PubMed
Luepker [pers comm]
-
- Luepker R. Queries re: MN Home Team [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, February 28, 2019.
Luttikhuis 2009
Lytle 1994
Lytle 1996
-
- Lytle LA, Stone EJ, Nichaman MZ, Perry CL, Montgomery DH, Nicklas TA, et al. Changes in nutrient intakes of elementary school children following a school‐based intervention: results from the CATCH Study. Preventive Medicine 1996;25(4):465‐77. [DOI: 10.1006/pmed.1996.0078; PUBMED: 8818069] - DOI - PubMed
Malik 2010
Malik 2013
Marmot 2007
-
- Marmot M, Atinmo T, Byers T, Chen J, Hirohata T, Jackson A, et al. Food, Nutrition, Physical activity, and the Prevention of Cancer: a Global Perspective. Washington DC: World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research, 2007.
Mayén 2014
McLean 2003
-
- McLean N, Griffin S, Toney K, Hardeman W. Family involvement in weight control, weight maintenance and weight‐loss interventions: a systematic review of randomised trials. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders 2003;27(9):987‐1005. [DOI: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802383; PUBMED: 12917703] - DOI - PubMed
Micha 2012
Micha 2015
-
- Micha R, Khatibzadeh S, Shi P, Andrews KG, Engell RE, Mozzaffarian D, Global Burden of Diseases Nutrition and Chronic Diseases Expert Group (NutriCoDE). Global, regional, and national consumption of major food groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis including 266 country‐specific nutrition surveys worldwide. BMJ Open 2015;5(9):e008705. [DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-008705; PMC4593162; PUBMED: 26408285] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Michie 2011
-
- Michie S, Ashford S, Sniehotta FF, Dombrowski SU, Bishop A, French DP. A refined taxonomy of behaviour change techniques to help people change their physical activity and healthy eating behaviours: the CALO‐RE taxonomy. Psychology and Health 2011;26(11):1479‐98. [DOI: 10.1080/08870446.2010.540664; PUBMED: 21678185] - DOI - PubMed
Michie 2013
-
- Michie S, Richardson M, Johnston M, Abraham C, Francis J, Hardeman W, et al. The behavior change technique taxonomy (v1) of 93 hierarchically clustered techniques: building an international consensus for the reporting of behavior change interventions. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 2013;46(1):81‐95. [DOI: 10.1007/s12160-013-9486-6; PUBMED: 23512568] - DOI - PubMed
Michie 2015
-
- Michie S, Wood CE, Johnson M, Abraham C, Francis JJ, Hardeman W. Behaviour change techniques: the development and evaluation of a taxonomic method for reporting and describing behaviour change interventions (a suite of five studies involving consensus methods, randomised controlled trials and analysis of qualitative data). Health Technology Assessment 2015;19(99):1‐188. [DOI: 10.3310/hta19990; PMC4781650; PUBMED: 26616119] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Mielke 2016
Mikkilä 2005
Moher 2009
Morris 2015
-
- Morris H, Skouteris H, Edwards S, Rutherford L. Obesity prevention interventions in early childhood education and care settings with parental involvement: a systematic review. Early Child Development and Care 2015;185(8):1283–313. [DOI: 10.1080/03004430.2014.991723] - DOI
Mozaffarian 2009
Nader 1996
-
- Nader PR, Sellers DE, Johnson CC, Perry CL, Stone EJ, Cook KC, et al. The effect of adult participation in a school‐based family intervention to improve children's diet and physical activity: the Child and Adolescent Trial for Cardiovascular Health. Preventive Medicine 1996;25(4):455‐64. [DOI: 10.1006/pmed.1996.0077; PUBMED: 8818068] - DOI - PubMed
Nader 1999
National Research Council 2004
-
- National Research Council, Institute of Medicine. Children's Health, the Nation's Wealth: Assessing and Improving Child Health. Washington DC: National Academies Press, 2004.
NCD Countdown 2030 Collaborators 2018
NCT00987532
-
- NCT00987532. A participatory parental intervention promoting physical activity in preschools. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00987532 (first received September 30, 2009).
NCT01588379
-
- NCT01588379. Mothers and girls dancing together trial (MAGNET) [Effects of an Afro‐centric dance program for African‐American daughters and mothers]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01588379 (first received April 25, 2012).
NCT02405611
-
- NCT02405611. A multi‐component intervention on improving fruit and vegetable consumption in teenagers and their mothers. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02405611 (first received March 25, 2015).
NCT02491294
-
- NCT02491294. Fuel for fun: cooking with kids plus parents and play (FFF) [Cooking with kids 2.0: plus parents and play]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02491294 (first received July 1, 2015).
NCT03075085
-
- NCT03075085. Developing and testing implementation strategies for evidence‐based obesity prevention in childcare. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03075085 (first received February 20, 2017).
NCT03111264
-
- NCT03111264. Building blocks for healthy preschoolers [Building blocks for healthy preschoolers: child care and family models]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03111264 (first received March 27, 2017).
NCT03590834
-
- NCT03590834. Míranos! program, a preschool obesity prevention RCT [Obesity prevention in Head Start: Míranos! program]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03590834 (first received June 27, 2018).
Ng 2014
-
- Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980‐2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014;384(9945):766–81. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60460-8; PMC4624264; PUBMED: 24880830] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Niemeier 2012
Nocon 2008
-
- Nocon M, Hiemann T, Müller‐Riemenschneider F, Thalau F, Roll S, Willich S. Association of physical activity with all‐cause and cardiovascular mortality: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. European Journal of Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation 2008;15(3):239–46. [DOI: 10.1097/HJR.0b013e3282f55e09; PUBMED: 18525377] - DOI - PubMed
NTR3938
-
- NTR3938. Strengthening parenting styles and practices in existing interventions to prevent overweight and obesity in children [Strengthening parenting styles and practices in existing interventions to prevent overweight and obesity in children, a cluster randomized study]. www.trialregister.nl/trial/3752 (first received April 7, 2013).
O'Connor 2009
Olshansky 2005
Pakpour 2019 [pers comm]
-
- Pakpour A. Queries about your HAPA intervention for adolescents [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, November 11, 2019.
Patrick 2005
-
- Patrick H, Nicklas TA. A review of family and social determinants of children's eating patterns and diet quality. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 2005;24(2):83–92. [PUBMED: 15798074] - PubMed
Pearson 2009
Perry 1988b
Perry 1989
-
- Perry CL, Luepker RV, Murray DM, Hearn MD, Halper A, Dudovitz B, et al. Parent involvement with children's health promotion: a one‐year follow‐up of the Minnesota home team. Health Education Quarterly 1989;16(2):171‐80. [PUBMED: 2732061] - PubMed
Perry 1992
-
- Perry CL, Parcel GS, Stone E, Nader P, McKinlay SM, Luepker RV, et al. The Child and Adolescent Trial for Cardiovascular Health (CATCH): overview of the intervention program and evaluation methods. Cardiovascular Risk Factors 1992;2(1):36‐44.
Perry 1997
-
- Perry CL, Sellers DE, Johnson C, Pedersen S, Bachman KJ, Parcel GS, et al. The Child and Adolescent Trial for Cardiovascular Health (CATCH): intervention, implementation, and feasibility for elementary schools in the United States. Health Education & Behavior 1997;24(6):716‐35. [DOI: 10.1177/109019819702400607; PUBMED: 9408786] - DOI - PubMed
Popkin 2013
Powles 2013
Puder 2010
Pulgarón 2014
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Roberto 2015
-
- Roberto CA, Swinburn B, Hawkes C, Huang TT‐K, Costa SA, Ashe M, et al. Patchy progress on obesity prevention: emerging examples, entrenched barriers, and new thinking. The Lancet 2015;385(9985):2400‐9. [10.1016/ S0140‐6736(14)61744‐X; PUBMED: 25703111] - PubMed
Ruiter 2015b
-
- Ruiter EL, Fransen GA, Molleman GR, Velden K, Engels RC. The effectiveness of a web‐based Dutch parenting program to prevent overweight in children 9‐13 years of age: study protocol for a two‐armed cluster randomized controlled trial. BMC Public Health 2015;15:148. [DOI: 10.1186/s12889-015-1394-1; PMC4335372; PUBMED: 25884190] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Rychetnik 2002
Sameroff 2010
Scaglioni 2011
Schultz 2010
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, et al. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Sharma 2006
Simmonds 2016
Skouteris 2011
Smith 2015
Sofi 2008
-
- Sofi F, Capalbo A, Cesari F, Abbate R, Gensini GF. Physical activity during leisure time and primary prevention of coronary heart disease: an updated meta‐analysis of cohort studies. European Journal of Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation 2008;15(3):247–57. [DOI: 10.1097/HJR.0b013e3282f232ac; PUBMED: 18525378] - DOI - PubMed
Solorzano 2010
Stalsberg 2010
Stice 2006
Swindle 2017
-
- Swindle T, Johnson SL, Whiteside‐Mansell L, Curran GM. A mixed methods protocol for developing and testing implementation strategies for evidence‐based obesity prevention in childcare: a cluster randomized hybrid type III trial. Implemention Science 2017;12(1):90. [DOI: 10.1186/s13012-017-0624-6; NCT03075085; PMC5516351 ; PUBMED: 28720140] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Tandon 2012
-
- Tandon PS, Zhou C, Sallis JF, Cain KL, Frank LD, Saelens BE. Home environment relationships with children's physical activity, sedentary time, and screen time by socioeconomic status. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2012;9:88. [DOI: 10.1186/1479-5868-9-88; PMC3413573; PUBMED: 22835155] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Teegala 2009
-
- Teegala SM, Willett WC, Mozaffarian D. Consumption and health effects of trans fatty acids: a review. Journal of AOAC International 2009;92(5):1250‐7. [PUBMED: 19916363] - PubMed
Thune 2001
-
- Thune I, Furberg AS. Physical activity and cancer risk: dose‐response and cancer, all sites and site‐specific. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2001;33(6 Suppl):S530–50. [PUBMED: 11427781] - PubMed
Tremblay 2014
Tzioumis 2014
UN General Assembly 2012
-
- UN General Assembly. Political declaration of the high‐level meeting of the General Assembly on the prevention and control of non‐communicable diseases. www.who.int/nmh/events/un_ncd_summit2011/political_declaration_en.pdf (accessed January 16, 2017).
United Nations 2015
-
- United Nations. Transforming our world: the 2030 agenda for sustainable development. sustainabledevelopment.un.org/post2015/transformingourworld/publication (accessed March 21, 2019).
Van Lippevelde 2012
-
- Lippevelde W, Verloigne M, Bourdeaudhuij I, Brug J, Bjelland M, Lien N, et al. Does parental involvement make a difference in school‐based nutrition and physical activity interventions? A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. International Journal of Public Health 2012;57(4):673‐8. [DOI: 10.1007/s00038-012-0335-3; PUBMED: 22301709] - DOI - PubMed
Vandongen 1995b
-
- Vandongen R, Jenner DA, Thompson C, Taggart AC, Spickett EE, Burke V, et al. A controlled evaluation of a fitness and nutrition intervention program on cardiovascular health in 10‐ to 12‐year‐old children. Preventive Medicine 1995;24(1):9‐22. [DOI: 10.1006/pmed.1995.1003; PUBMED: 7740021] - DOI - PubMed
Wang 2007b
-
- Wang C, Zhao H, Liu P, Ju P, He Z, Cong N. Effect of three ways of nutritional education on knowledge‐attitude‐behavior with nutrition in pupils. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu [Journal of Hygiene Research] 2007;36(1):85‐7. [PUBMED: 17424859] - PubMed
Wang 2014
-
- Wang X, Ouyang Y, Liu J, Zhu M, Zhao G, Bao W, et al. Fruit and vegetable consumption and mortality from all causes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer: systematic review and dose‐response meta‐analysis of prospective cohort studies. BMJ 2014;349:g4490. [DOI: 10.1136/bmj.g4490; PMC4115152; PUBMED: 25073782] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Waters 2011
Werch 2003b
-
- Werch C, Moore M, DiClemente CC, Owen DM, Jobli E, Bledsoe R. A sport‐based intervention for preventing alcohol use and promoting physical activity among adolescents. Journal of School Health 2003;73(10):380‐8. [PUBMED: 14727390] - PubMed
Werch 2018 [pers comm]
-
- Werch C. New customer message on May 17, 2018 at 02:00 PM [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, May 17, 2018.
WHO 2003
-
- World Health Organization. Diet, Nutrition, and the Prevention of Chronic Diseases: Report of the Joint WHO/FAO Expert Consultation. World Health Organization: Geneva, 2003.
WHO 2010
-
- WHO. Global recommendations on physical activity for health. www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/global‐PA‐recs‐2010.pdf (accessed February 12, 2019).
WHO 2013
-
- World Health Organization. Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases 2013‐2020. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2013.
WHO 2016
-
- World Health Organization. Report of the Commission on Ending Childhood Obesity. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2016.
WHO 2018
-
- WHO. Healthy diet: key facts. www.who.int/news‐room/fact‐sheets/detail/healthy‐diet (accessed February 12, 2019).
WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group 2006
-
- WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group. WHO Child Growth Standards: Length/height‐for‐age, Weight‐for‐age, Weight‐for‐length, Weight‐for‐height and Body Mass Index‐for‐age: Methods and Development. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2006. [PUBMED: 16817681] - PubMed
Wilkinson 2011
-
- Wilkinson RG, Pickett K. The Spirit Level: Why Greater Equality Makes Societies Stronger. London, UK: Bloomsbury Press, 2011.
Wilmot 2012
-
- Wilmot EG, Edwardson CL, Achana FA, Davies MJ, Gorely T, Gray LJ, et al. Sedentary time in adults and the association with diabetes, cardiovascular disease and death: systematic review and meta‐analysis. Diabetologia 2012;55(11):2895–905. [DOI: 10.1007/s00125-012-2677-z; PUBMED: 22890825] - DOI - PubMed
Wu 2015
Xi 2015
Yavuz 2015
Ye 2012
Yeh 2018b
Yeh 2018c [pers comm]
-
- Yeh Y. Query re: Study at Head Start sites in Detroit [personal communication]. Email to E Morgan, August 18, 2018.
Yin 2019
-
- Yin Z, Ullevig SL, Sosa E, Liang Y, Olmstead T, Howard JT, et al. Study protocol for a cluster randomized controlled trial to test "¡Míranos! Look at Us, We Are Healthy!"—an early childhood obesity prevention program. BMC Pediatrics 2019;19(1):190. [DOI: 10.1186/s12887-019-1541-4; NCT03590834; PMC6556954 ; PUBMED: 31179916] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Young 2007
Zhao 2006
-
- Zhao H. Intervention Study on Improvement of Knowledge, Attitude and Practice With Calcium Nutrition in Pupil [Masters thesis]. Nanjing, JS: Southeast University, 2006.
Zucker 1995
-
- Zucker DM, Lakatos E, Webber LS, Murray DM, McKinlay SM, Feldman HA, et al. Statistical design of the Child and Adolescent Trial for Cardiovascular Health (CATCH): implications of cluster randomization. Controlled Clinical Trials 1995;16(2):96‐118. [PUBMED: 7789139] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

