Etiology, epidemiology, pathology, and advances in diagnosis, vaccine development, and treatment of Gallibacterium anatis infection in poultry: a review
- PMID: 31902298
- PMCID: PMC7006735
- DOI: 10.1080/01652176.2020.1712495
Etiology, epidemiology, pathology, and advances in diagnosis, vaccine development, and treatment of Gallibacterium anatis infection in poultry: a review
Abstract
Gallibacterium anatis is a Gram-negative bacterium of the Pasteurellaceae family that resides normally in the respiratory and reproductive tracts in poultry. It is a major cause of oophoritis, salpingitis, and peritonitis, decreases egg production and mortality in hens thereby severely affecting animal welfare and overall productivity by poultry industries across Europe, Asia, America, and Africa. In addition, it has the ability to infect wider host range including domesticated and free-ranging avian hosts as well as mammalian hosts such as cattle, pigs and human. Evaluating the common virulence factors including outer membrane vesicles, fimbriae, capsule, metalloproteases, biofilm formation, hemagglutinin, and determining novel factors such as the RTX-like toxin GtxA, elongation factor-Tu, and clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) has pathobiological, diagnostic, prophylactic, and therapeutic significance. Treating this bacterial pathogen with traditional antimicrobial drugs is discouraged owing to the emergence of widespread multidrug resistance, whereas the efficacy of preventing this disease by classical vaccines is limited due to its antigenic diversity. It will be necessary to acquire in-depth knowledge on important virulence factors, pathogenesis and, concerns of rising antibiotic resistance, improvised treatment regimes, and novel vaccine candidates to effectively tackle this pathogen. This review substantially describes the etio-epidemiological aspects of G. anatis infection in poultry, and updates the recent development in understanding the pathogenesis, organism evolution and therapeutic and prophylactic approaches to counter G. anatis infection for safeguarding the welfare and health of poultry.
Keywords: Gallibacterium anatis; control; diagnosis; epidemiology; pathogenesis; pathology; poultry; prevention; review; treatment; virulence factors.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there exist no commercial or financial relationships that could, in any way, lead to a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
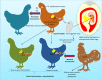
 Indicates presence of G. anatis in the upper respiratory tract without causing significant clinical signs.
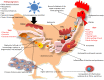
Indicates presence of G. anatis in the upper respiratory tract without causing significant clinical signs.  Indicates organs affected and their pathological changes.
Indicates organs affected and their pathological changes.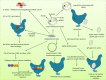
References
-
- Abdul-Aziz T, Fletcher OJ, Barnes HJ, Shivaprasad HL, Swayne DE.. 2016. Avian histopathology. 4th ed. Florida (US): American Association of Avian Pathologists, p. 456.
-
- Addo PB, Mohan K.. 1985. Atypical Pasteurella hemolytica type A from poultry. Avian Dis. 29(1):214–217. - PubMed
-
- Aktories K, Lang AE, Schwan C, Mannherz HG.. 2011. Actin as target for modification by bacterial protein toxins. FEBS J. 278(23):4526–4543. - PubMed
-
- Alispahic M, Christensen H, Hess C, Razzazi-Fazeli E, Bisgaard M, Hess M.. 2011. Identification of Gallibacterium species by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry evaluated by multilocus sequence analysis. Int J Med Microbiol. 301(6):513–522. - PubMed
-
- Alispahic M, Christensen H, Hess C, Razzazi-Fazeli E, Bisgaard M, Hess M.. 2012. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry confirms clonal lineages of Gallibacterium anatis between chicken flocks. Vet Microbiol. 160(1-2):269–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
