Neonatal retinoblastoma: A study of five cases
- PMID: 31902989
- PMCID: PMC6826596
- DOI: 10.4103/ojo.OJO_176_2018
Neonatal retinoblastoma: A study of five cases
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose was to study the clinical features, treatment, and outcome of retinoblastoma (RB) in neonates.
Methods: This was a retrospective study of five patients with RB detected in the 1st month of life.
Results: The mean age at diagnosis of RB was 22 days (median, 24 days; range, 14-28 days). There were one female and four males with neonatal RB. Two patients had a known family history of RB, and the tumor was detected by routine fundus screening in these children. Two patients were brought in with complaints of leukocoria and one patient with complaints of red-eye. All patients had an intraocular tumor at presentation. Four patients had bilateral involvement, whereas only one had unilateral involvement. Based on the International Classification of Intraocular Retinoblastoma, the tumors were classified as Group A (n = 2), Group B (n = 3), Group C (n = 1), Group D (n = 1), and Group E (n = 2). Macular involvement was noted in 6 (67%) eyes. The primary treatment included systemic chemotherapy with/without focal treatment in all patients. One patient subsequently underwent secondary enucleation as the globe became phthisical. One child died while on treatment due to pneumonia secondary to chemotherapy-induced neutropenia. Of the four patients who completed treatment, globe salvage was achieved in 6 (86%) eyes over a mean follow-up period of 89 months (median, 92 months; range, 29-144 months).
Conclusion: Neonatal RB though rare, if detected early, has a favorable outcome of ocular and life salvage. Sporadic RB can occur in neonates, and a family history may not always be elicited.
Keywords: Eye; neonates; retina; retinoblastoma; tumor.
Copyright: © 2019 Oman Ophthalmic Society.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
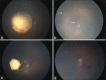
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bilateral enucleation for retinoblastoma: A study of 14 patients.Oman J Ophthalmol. 2022 Jun 29;15(2):188-192. doi: 10.4103/ojo.ojo_272_21. eCollection 2022 May-Aug. Oman J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35937719 Free PMC article.
-
RETINOBLASTOMA IN INDIA: Clinical Presentation and Outcome in 1,457 Patients (2,074 Eyes).Retina. 2019 Feb;39(2):379-391. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000001962. Retina. 2019. PMID: 29210937
-
Primary Macular Retinoblastoma: Clinical Presentation and Treatment Outcomes.J Vitreoretin Dis. 2022 Aug 4;6(5):367-373. doi: 10.1177/24741264221107757. eCollection 2022 Sep-Oct. J Vitreoretin Dis. 2022. PMID: 37006899 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoblastoma: Review and new insights.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 2;12:963780. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.963780. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36408154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neonatal Retinoblastoma.Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2017 Jul-Sep;4(3):197-204. doi: 10.4103/apjon.apjon_18_17. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2017. PMID: 28695165 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
At What Age Could Screening for Familial Retinoblastoma Be Discontinued? A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 17;13(8):1942. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081942. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33920538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moore SW, Satgé D, Sasco AJ, Zimmermann A, Plaschkes J. The epidemiology of neonatal tumours. Report of an international working group. Pediatr Surg Int. 2003;19:509–19. - PubMed
-
- Orbach D, Sarnacki S, Brisse HJ, Gauthier-Villars M, Jarreau PH, Tsatsaris V, et al. Neonatal cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:e609–20. - PubMed
-
- Kivelä T. The epidemiological challenge of the most frequent eye cancer: Retinoblastoma, an issue of birth and death. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009;93:1129–31. - PubMed

