Theranostic application of miR-429 in HER2+ breast cancer
- PMID: 31903105
- PMCID: PMC6929607
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.36274
Theranostic application of miR-429 in HER2+ breast cancer
Abstract
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is overexpressed/amplified in one third of breast cancers (BCs), and is associated with the poorer prognosis and the higher metastatic potential in BC. Emerging evidences highlight the role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in the regulation of several cellular processes, including BC.
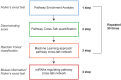
Methods: Here we identified, by in silico approach, a group of three miRNAs with central biological role (high degree centrality) in HER2+ BC. We validated their dysregulation in HER2+ BC and we analysed their functional role by in vitro approaches on selected cell lines and by in vivo experiments in an animal model.
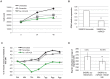
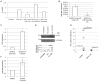
Results: We found that their expression is dysregulated in both HER2+ BC cell lines and human samples. Focusing our study on the only upregulated miRNA, miR-429, we discovered that it acts as an oncogene and its upregulation is required for HER2+ cell proliferation. It controls the metastatic potential of HER2+ BC subtype by regulating migration and invasion of the cell.
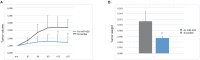
Conclusions: In HER2+ BC oncogenic miR-429 is able to regulate HIF1α pathway by directly targeting VHL mRNA, a molecule important for the degradation of HIF1α. The overexpression of miR-429, observed in HER2+ BC, causes increased proliferation and migration of the BC cells. More important, silencing miR-429 succeeds in delaying tumor growth, thus miR-429 could be proposed as a therapeutic probe in HER2+ BC tumors.
Keywords: HER2+ breast cancer; Theranostics; diagnosis; microRNAs; therapeutic tool.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




References
-
- Tandon AK, Clark GM, Chamness GC, Ullrich A, McGuire WL. HER-2/neu oncogene protein and prognosis in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1989;7:1120–8. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed AR. HER2 expression is a strong independent predictor of nodal metastasis in breast cancer. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2016;28:219–27. - PubMed
-
- Aversa C, Rossi V, Geuna E, Martinello R, Milani A, Redana S. et al. Metastatic breast cancer subtypes and central nervous system metastases. Breast. 2014;23:623–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

