Influence of polydimethylsiloxane substrate stiffness on corneal epithelial cells
- PMID: 31903218
- PMCID: PMC6936283
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.191796
Influence of polydimethylsiloxane substrate stiffness on corneal epithelial cells
Abstract
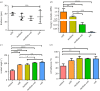
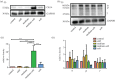
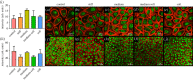
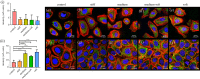
Many cell types are known to modulate their behaviour in response to changes in material stiffness; however, little is known about how stiffness affects corneal epithelial cells. This study aims to investigate the response of a corneal epithelial cell line to polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) substrates with a range of Young's moduli from 10 to 1500 kPa. Cellular morphology, proliferation, differentiation and mechanobiology were examined. Cells grown on PDMS adopted the typical cobblestone morphology exhibited by the corneal epithelium. Proliferative markers pERK and Ki67 were higher in cells cultured on stiffer substrates compared with those on softer substrates. Material stiffness was also found to influence the cell phenotype with cells on stiffer substrates having higher cytokeratin 3 gene expression, a mature epithelial marker, while cells on softer substrates expressed more cytokeratin 14, a basal epithelial marker. Cells grown on softer substrates also displayed higher levels of focal adhesions and intermediate filaments compared with cells on stiff substrates. This research will aid in designing novel biomaterials for the culture and transplantation of corneal epithelial cells.
Keywords: cornea; epithelium; mechanobiology; substrate stiffness.
© 2019 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hepatic C9 cells switch their behaviour in short or long exposure to soft substrates.Biol Cell. 2020 Oct;112(10):265-279. doi: 10.1111/boc.201900115. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Biol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32449790
-
Respective Effects of Gelatin-Coated Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Substrates on Self-renewal and Cardiac Differentiation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs).ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018 Dec 10;4(12):4321-4330. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b00993. Epub 2018 Oct 16. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018. PMID: 33418827
-
Substrate stiffness regulates B-cell activation, proliferation, class switch, and T-cell-independent antibody responses in vivo.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Jun;45(6):1621-34. doi: 10.1002/eji.201444777. Epub 2015 Apr 15. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25756957
-
Evaluation of polydimethylsiloxane-based substrates for in vitro culture of human periodontal ligament cells.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019 Dec;107(12):2796-2805. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.36782. Epub 2019 Aug 27. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019. PMID: 31408269
-
Characterization, isolation, expansion and clinical therapy of human corneal epithelial stem/progenitor cells.J Stem Cells. 2014;9(2):79-91. J Stem Cells. 2014. PMID: 25158157 Review.
Cited by
-
Toward Corneal Limbus In Vitro Model: Regulation of hPSC-LSC Phenotype by Matrix Stiffness and Topography During Cell Differentiation Process.Adv Healthc Mater. 2023 Nov;12(29):e2301396. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202301396. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023. PMID: 37449943 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive protocol for PDMS fabrication for use in cell culture.PLoS One. 2025 May 12;20(5):e0323283. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323283. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40354467 Free PMC article.
-
Squishy matters - Corneal mechanobiology in health and disease.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2024 Mar;99:101234. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2023.101234. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2024. PMID: 38176611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-Assembling Polypeptide Hydrogels as a Platform to Recapitulate the Tumor Microenvironment.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 30;13(13):3286. doi: 10.3390/cancers13133286. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34209094 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the mechanobiology of cornea: From bench side to the clinic.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Oct 3;10:953590. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.953590. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36263359 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

