It is all about patients' stories: Case-based learning in residents' education
- PMID: 31903323
- PMCID: PMC6916428
- DOI: 10.5339/qmj.2019.17
It is all about patients' stories: Case-based learning in residents' education
Abstract
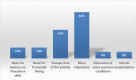
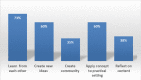
Background: Problem-based learning (PBL) is an inquiry-based learning strategy which is learner centered and facilitates group discussion and critical thinking. Case-based learning (CBL), which is a more guided approach of PBL, enables students to learn within the context of patients and formulate their knowledge around patients' scenarios. Midweek (MW) activity is an important educational activity in the internal medicine residency program (IMRP). CBL has shown many benefits in postgraduate education. The aim of our study was to describe the implementation of a teaching resident's management of acute medical conditions encountered during their call utilizing the CBL format and to evaluate resident satisfaction with the new teaching style. Methods: This study describes the implementation of CBL in residents' education at the IMRP. CBL was introduced in five of the 10 acute medical sessions taught in the noon activity. A mixed-method study was employed using both a structured questionnaire and a focus group to compare the two methods to evaluate the residents' satisfaction and perception of knowledge acquisition. Results: The focus group discussion showed that sessions conducted in CBL format were more engaging, interactive, and resulted in better knowledge acquisition through sharing and peer-to-peer teaching than the traditional lecture format. Thirty-nine out of 83 (47%) residents ranging from PGY2 to PGY4 responded to the survey. Overall satisfaction with CBL was good. Sixty-four percent preferred it over the lecture format; 87% found that they did improve their knowledge; 84% agreed that they were excellent and more interactive. Seventy-nine percent stated that they would like to have this type of teaching in the MW activity sessions. Conclusion: Based on the present study, we conclude that incorporation of CBL resulted in more engagement, interaction, peer-to-peer education, and overall residents' satisfaction. The key elements for a successful implementation of this format are both instructors' and residents' orientation and careful selection of the case scenarios (problems) that trigger the learning process. Incorporation of various teaching strategies in residents' education is mandatory to enhance learning and create excellent educational experiences.
Keywords: Accreditation Council of Graduate Medical Education; Accreditation Council of Graduate Medical Education- International; case-based learning; problem-based learning; teaching strategies.
© 2019 Suliman, Al-Mohammed, Al Mohanadi, Karim, Elbuzidi, Mubasher, Rahil, licensee HBKU Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Actively Teaching Active Teaching Techniques.J Educ Teach Emerg Med. 2024 Oct 31;9(4):SG1-SG12. doi: 10.21980/J8H94V. eCollection 2024 Oct. J Educ Teach Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 39507470 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of the combined problem-based learning (PBL) and case-based learning (CBL) teaching method in the clinical practical teaching of thyroid disease.BMC Med Educ. 2020 Oct 22;20(1):381. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02306-y. BMC Med Educ. 2020. PMID: 33092583 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Novel Virtual Emergency Medicine Residents-as-Teachers (RAT) Curriculum.J Educ Teach Emerg Med. 2021 Jul 15;6(3):C9-C63. doi: 10.21980/J86S71. eCollection 2021 Jul. J Educ Teach Emerg Med. 2021. PMID: 37465066 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating Coding Accuracy in General Surgery Residents' Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education Procedural Case Logs.J Surg Educ. 2016 Nov-Dec;73(6):e59-e63. doi: 10.1016/j.jsurg.2016.07.017. J Surg Educ. 2016. PMID: 27886974 Review.
-
Case-based learning interventions for undergraduate nursing students in a theoretical course: A review of design, implementation, and outcomes.J Prof Nurs. 2023 May-Jun;46:119-133. doi: 10.1016/j.profnurs.2023.03.007. Epub 2023 Mar 23. J Prof Nurs. 2023. PMID: 37188400
Cited by
-
Students' perceptions of virtual interactive clinical case-based learning: A comparative study with three different cohorts.J Dent Sci. 2024 Jul;19(3):1578-1586. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2023.12.018. Epub 2023 Dec 27. J Dent Sci. 2024. PMID: 39035319 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a curriculum to improve cardiology fellows' training in pregnancy and cardiovascular disease.BMC Med Educ. 2022 Mar 10;22(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s12909-022-03228-7. BMC Med Educ. 2022. PMID: 35272659 Free PMC article.
-
A Shift in Medical Education During the COVID-19 Pandemic.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1318:773-784. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-63761-3_43. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33973211
-
Prevalence of and Barriers to Health Disparities Education Among Otolaryngology Residency Curricula.OTO Open. 2024 Jun 1;8(2):e148. doi: 10.1002/oto2.148. eCollection 2024 Apr-Jun. OTO Open. 2024. PMID: 38826640 Free PMC article.
-
Cultivating Professionalism in Saudi Arabian Neurology Residency Programs: The Impact of Case-Based Learning.Adv Med Educ Pract. 2025 Feb 21;16:287-295. doi: 10.2147/AMEP.S499212. eCollection 2025. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2025. PMID: 40007757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Handelsman J, Ebert-May D, Beichner R, Bruns P, Chang A, DeHaan R et al. Scientific teaching. Science. 2004;304(5670):521–522. - PubMed
-
- Chi MTH, Glaser R, Rees E. Expertise in problem solving. In: Sternberg RS, ed. Advances in the Psychology of Human Intelligence. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum; 1982:1–75.
-
- Hmelo-Silver CE. Problem-based learning: what and how do students learn? Educ Psychol Rev. 2004;16(3):235–266.
-
- Barbour RS. Making sense of focus groups. Med Educ. 2005;39(7):742–750. - PubMed
-
- Thistlethwaite JE, Davies D, Ekeocha S, Kidd JM, MacDougall C, Matthews P et al. The effectiveness of case-based learning in health professional education: A BEME systematic review: BEME Guide 23. Med Teach. 2012;34(6):e421–e444. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous