Transendothelial Insulin Transport is Impaired in Skeletal Muscle Capillaries of Obese Male Mice
- PMID: 31903723
- PMCID: PMC6980999
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.22683
Transendothelial Insulin Transport is Impaired in Skeletal Muscle Capillaries of Obese Male Mice
Abstract
Objective: The continuous endothelium of skeletal muscle (SkM) capillaries regulates insulin's access to skeletal myocytes. Whether impaired transendothelial insulin transport (EIT) contributes to SkM insulin resistance (IR), however, is unknown.
Methods: Male and female C57/Bl6 mice were fed either chow or a high-fat diet for 16 weeks. Intravital microscopy was used to measure EIT in SkM capillaries, electron microscopy to assess endothelial ultrastructure, and glucose tracers to measure indices of glucose metabolism.
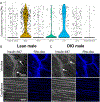
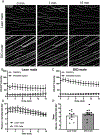
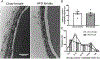
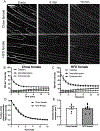
Results: Diet-induced obesity (DIO) male mice were found to have a ~15% reduction in EIT compared with lean mice. Impaired EIT was associated with a 45% reduction in endothelial vesicles. Despite impaired EIT, hyperinsulinemia sustained delivery of insulin to the interstitial space in DIO male mice. Even with sustained interstitial insulin delivery, DIO male mice still showed SkM IR indicating severe myocellular IR in this model. Interestingly, there was no difference in EIT, endothelial ultrastructure, or SkM insulin sensitivity between lean female mice and female mice fed a high-fat diet.
Conclusions: These results suggest that, in male mice, obesity results in ultrastructural alterations to the capillary endothelium that delay EIT. Nonetheless, the myocyte appears to exceed the endothelium as a contributor to SkM IR in DIO male mice.
© 2020 The Authors. Obesity published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Obesity Society (TOS).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Chen YL, and Messina EJ (1996) Dilation of isolated skeletal muscle arterioles by insulin is endothelium dependent and nitric oxide mediated. Am. J. Physiol 270, H2120–4 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 DK050277/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F31DK109594/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U2C DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 18SFRN33960210/American Heart Association/International
- U24DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK054902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007563/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32DK007563/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DK109594/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37DK050277/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

