DORN1/P2K1 and purino-calcium signalling in plants: making waves with extracellular ATP
- PMID: 31904093
- PMCID: PMC6943698
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcz135
DORN1/P2K1 and purino-calcium signalling in plants: making waves with extracellular ATP
Abstract
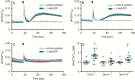
Background and aims: Extracellular ATP governs a range of plant functions, including cell viability, adaptation and cross-kingdom interactions. Key functions of extracellular ATP in leaves and roots may involve an increase in cytosolic free calcium as a second messenger ('calcium signature'). The main aim here was to determine to what extent leaf and root calcium responses require the DORN1/P2K1 extracellular ATP receptor in Arabidopsis thaliana. The second aim was to test whether extracellular ATP can generate a calcium wave in the root.
Methods: Leaf and root responses to extracellular ATP were reviewed for their possible links to calcium signalling and DORN1/P2K1. Leaves and roots of wild type and dorn1 plants were tested for cytosolic calcium increase in response to ATP, using aequorin. The spatial abundance of DORN1/P2K1 in the root was estimated using green fluorescent protein. Wild type roots expressing GCaMP3 were used to determine the spatial variation of cytosolic calcium increase in response to extracellular ATP.
Key results: Leaf and root ATP-induced calcium signatures differed markedly. The leaf signature was only partially dependent on DORN1/P2K1, while the root signature was fully dependent. The distribution of DORN1/P2K1 in the root supports a key role in the generation of the apical calcium signature. Root apical and sub-apical calcium signatures may operate independently of each other but an apical calcium increase can drive a sub-apical increase, consistent with a calcium wave.
Conclusion: DORN1 could underpin several calcium-related responses but it may not be the only receptor for extracellular ATP in Arabidopsis. The root has the capacity for a calcium wave, triggered by extracellular ATP at the apex.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; ATP; DORN1; P2K1; calcium; reactive oxygen species; root; wave.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Annals of Botany Company.
Figures




References
-
- Behera S, Wang N, Zhang C, et al. . 2015. Analyses of Ca2+ dynamics using a ubiquitin-10 promoter-driven Yellow Cameleon 3.6 indicator reveal reliable transgene expression and differences in cytoplasmic Ca2+ responses in Arabidopsis and rice (Oryza sativa) roots. New Phytologist 206: 751–760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

