2-Deoxy-d-Glucose and Its Analogs: From Diagnostic to Therapeutic Agents
- PMID: 31905745
- PMCID: PMC6982256
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21010234
2-Deoxy-d-Glucose and Its Analogs: From Diagnostic to Therapeutic Agents
Abstract
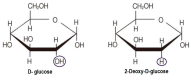
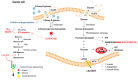
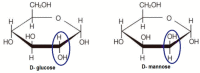
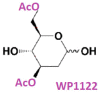
The ability of 2-deoxy-d-glucose (2-DG) to interfere with d-glucose metabolism demonstrates that nutrient and energy deprivation is an efficient tool to suppress cancer cell growth and survival. Acting as a d-glucose mimic, 2-DG inhibits glycolysis due to formation and intracellular accumulation of 2-deoxy-d-glucose-6-phosphate (2-DG6P), inhibiting the function of hexokinase and glucose-6-phosphate isomerase, and inducing cell death. In addition to glycolysis inhibition, other molecular processes are also affected by 2-DG. Attempts to improve 2-DG's drug-like properties, its role as a potential adjuvant for other chemotherapeutics, and novel 2-DG analogs as promising new anticancer agents are discussed in this review.
Keywords: 2-DG analogs; 2-deoxy-d-glucose; anticancer therapy; glioblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Priebe is listed as an inventor on patents covering new analogs of 2-DG. He is also a share holder of Moleculin Biotech Inc., and his research is in part supported by the sponsor research grant from Moleculin Biotech, Inc. Fokt is listed as an inventor on patents covering new analogs of 2-DG. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Warburg O. Versuche an uberlebendem carcinomgewebe. Klin. Wochenschr. 1923;2:776–777. doi: 10.1007/BF01712130. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

