High Throughput Phenotyping for Various Traits on Soybean Seeds Using Image Analysis
- PMID: 31906262
- PMCID: PMC6982885
- DOI: 10.3390/s20010248
High Throughput Phenotyping for Various Traits on Soybean Seeds Using Image Analysis
Abstract
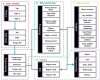
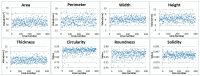
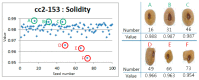
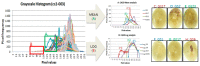
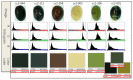
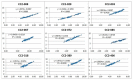
Data phenotyping traits on soybean seeds such as shape and color has been obscure because it is difficult to define them clearly. Further, it takes too much time and effort to have sufficient number of samplings especially length and width. These difficulties prevented seed morphology to be incorporated into efficient breeding program. Here, we propose methods for an image acquisition, a data processing, and analysis for the morphology and color of soybean seeds by high-throughput method using images analysis. As results, quantitative values for colors and various types of morphological traits could be screened to create a standard for subsequent evaluation of the genotype. Phenotyping method in the current study could define the morphology and color of soybean seeds in highly accurate and reliable manner. Further, this method enables the measurement and analysis of large amounts of plant seed phenotype data in a short time, which was not possible before. Fast and precise phenotype data obtained here may facilitate Genome Wide Association Study for the gene function analysis as well as for development of the elite varieties having desirable seed traits.
Keywords: RGB image; breeding; seed color; seed morphology; seed traits.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sakai N., Yonekawa S. Three-dimensional image analysis of the shape of soybean seed. J. Food Eng. 1992;15:221–234. doi: 10.1016/0260-8774(92)90052-8. - DOI
-
- Vollmann J., Walter H., Sato T., Schweiger P. Digital image analysis and chlorophyll metering for phenotyping the effects of nodulation in soybean. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2011;75:190–195. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2010.11.003. - DOI
-
- Shatadal P., Tan J. Identifying damaged soybeans by color image analysis. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2003;19:65. doi: 10.13031/2013.12724. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

