Crosstalk with Jasmonic Acid Integrates Multiple Responses in Plant Development
- PMID: 31906415
- PMCID: PMC6981462
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21010305
Crosstalk with Jasmonic Acid Integrates Multiple Responses in Plant Development
Abstract
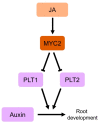
To date, extensive studies have identified many classes of hormones in plants and revealed the specific, nonredundant signaling pathways for each hormone. However, plant hormone functions largely overlap in many aspects of plant development and environmental responses, suggesting that studying the crosstalk among plant hormones is key to understanding hormonal responses in plants. The phytohormone jasmonic acid (JA) is deeply involved in the regulation of plant responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. In addition, a growing number of studies suggest that JA plays an essential role in the modulation of plant growth and development under stress conditions, and crosstalk between JA and other phytohormones involved in growth and development, such as gibberellic acid (GA), cytokinin, and auxin modulate various developmental processes. This review summarizes recent findings of JA crosstalk in the modulation of plant growth and development, focusing on JA-GA, JA-cytokinin, and JA-auxin crosstalk. The molecular mechanisms underlying this crosstalk are also discussed.
Keywords: auxin; crosstalk; cytokinin; gibberellic acid; jasmonic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Yang J., Duan G., Li C., Liu L., Han G., Zhang Y., Wang C. The Crosstalks Between Jasmonic Acid and Other Plant Hormone Signaling Highlight the Involvement of Jasmonic Acid as a Core Component in Plant Response to Biotic and Abiotic Stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2019;10:1349. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01349. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Genva M., Akong F.O., Andersson M.X., Deleu M., Lins L., Fauconnier M.-L. New insights into the biosynthesis of esterified oxylipins and their involvement in plant defense and developmental mechanisms. Phytochem. Rev. 2019;18:343–358. doi: 10.1007/s11101-018-9595-8. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

