Medication-related osteonecrosis (MRONJ) of the mandible and maxilla
- PMID: 31907213
- PMCID: PMC6954753
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-224455
Medication-related osteonecrosis (MRONJ) of the mandible and maxilla
Corrected and republished in
-
Republished: Medication-related osteonecrosis (MRONJ) of the mandible and maxilla.Drug Ther Bull. 2020 Nov;58(11):172-175. doi: 10.1136/dtb.2020.224455rep. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Drug Ther Bull. 2020. PMID: 32586952 No abstract available.
Abstract
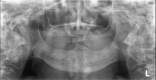
In 2003, Marx reported the first case of osteonecrosis of the jaw in 36 cases related to zoledronic acid or pamidronate. Painful bone exposure in the mandible or maxilla unresponsive to medical or surgical management was observed. In 2014, the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons proposed the term 'medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw' (MRONJ). However, a non-exposed variant may also occur. MRONJ can lead to debilitating clinical sequelae with limited treatment options. We present the case of a 73-year-old woman with metastatic breast cancer and MRONJ of her mandible and maxilla following treatment with intravenous zoledronic acid and denosumab. Six months following dental extractions, she was referred to the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery for assessment of extensive necrosis of her maxilla and mandible. Extraoral draining sinuses were observed. A CT mandible showed cortical destruction with an ill-defined mixed sclerotic-lucent pattern in keeping with osteonecrosis. Due to her metastatic breast cancer, the extent of her necrosis and poor performance status, free flap reconstruction of her mandible was ruled out. She was treated conservatively.
Keywords: dentistry and oral medicine; unwanted effects / adverse reactions.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2020. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Migliorati CA. Bisphosphonates and oral cavity avascular bone necrosis. J Clin Oncol 2003;22:4253–4. - PubMed
-
- Ruggiero SL, Dodson TB, Fantasia J, et al. . American association of oral and maxillofacial surgeons position paper on medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw—2009 update. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2009;67. - PubMed
-
- WX Q, Tang LN, An H, et al. . Risk of osteonecrosis of the jaw in cancer patients receiving denosumab: a meta-analysis of seven randomised controlled trials. Int J Clin Oncol 2014;19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
