A bipartite structural organization defines the SERINC family of HIV-1 restriction factors
- PMID: 31907454
- PMCID: PMC6956856
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-019-0357-0
A bipartite structural organization defines the SERINC family of HIV-1 restriction factors
Abstract
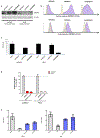
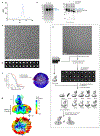
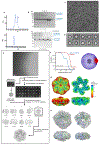
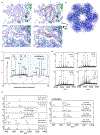
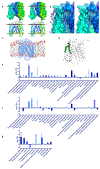
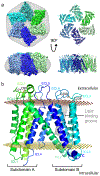
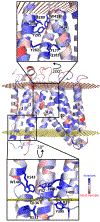
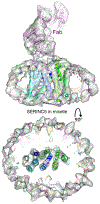
The human integral membrane protein SERINC5 potently restricts HIV-1 infectivity and sensitizes the virus to antibody-mediated neutralization. Here, using cryo-EM, we determine the structures of human SERINC5 and its orthologue from Drosophila melanogaster at subnanometer and near-atomic resolution, respectively. The structures reveal a novel fold comprised of ten transmembrane helices organized into two subdomains and bisected by a long diagonal helix. A lipid binding groove and clusters of conserved residues highlight potential functional sites. A structure-based mutagenesis scan identified surface-exposed regions and the interface between the subdomains of SERINC5 as critical for HIV-1-restriction activity. The same regions are also important for viral sensitization to neutralizing antibodies, directly linking the antiviral activity of SERINC5 with remodeling of the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

