Indian Subcontinent's First Bilateral Supracondylar Level Upper Limb Transplantation
- PMID: 31908366
- PMCID: PMC6938436
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0039-3401466
Indian Subcontinent's First Bilateral Supracondylar Level Upper Limb Transplantation
Abstract
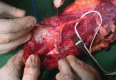
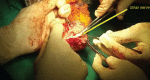
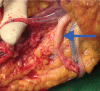
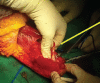
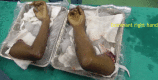
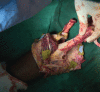
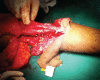
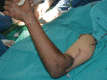
Introduction This is the first case of supracondylar level transplant from the Indian subcontinent, performed for a bilateral below elbow amputee. It has a completely different set of challenges for the transplant team, with a relatively shorter ischemia time window. The technical considerations for the same have been discussed in detail in this article. Materials and Methods The patient was a 19-year-old female who lost her both upper limbs at proximal forearm level due to severe crush injury following a road traffic accident. Insufficient bone length on either side necessitated a supracondylar level transplant. The preoperative workup included detailed clinical evaluation, biochemical, and psychological evaluation. The donor was a young brain-dead, male patient from a hospital, 30 minutes away. The donor and recipient preparations in this case were unique. The recipient's own elbow flexors and extensors were used while the elbow joint was from the donor. The specific challenges we faced during this procedure have been described in detail. Results The transplantation has been a complete technical success, with the patient rehabilitated back to her independent life style. This article describes only the technical considerations. The functional recovery aspect is part of an another soon to be published manuscript. Conclusion Supracondylar level arm-transplant requires a highly coordinated team effort with precise preoperative planning, along with meticulous attention to detail to achieve a successful outcome. In properly selected patients, it could be a life-changing procedure, worth all the effort.
Keywords: Indian hand transplantation; bilateral hand transplantation; hand transplantation; supracondylar hand transplantation; vascularized tissue allotransplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures












References
-
- Siemionow M Z, Kulahci Y, Bozkurt M.Composite tissue allotransplantation Plast Reconstr Surg 2009124(6, Suppl):e327–e339. - PubMed
-
- Shores J T, Higgins J P, Lee W P. Above-elbow (supracondylar) arm transplantation: clinical considerations and surgical technique. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2013;17(04):221–227. - PubMed
-
- Petruzzo P, Dubernard J M.The International Registry on Hand and Composite Tissue allotransplantation Clin Transpl 2011. •••:247–253. - PubMed
-
- Murphy B D, Zuker R M, Borschel G H. Vascularized composite allotransplantation: an update on medical and surgical progress and remaining challenges. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013;66(11):1449–1455. - PubMed
-
- Jones N F, Schneeberger S. Arm transplantation: prospects and visions. Transplant Proc. 2009;41(02):476–480. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

