A Novel Nanomicellar Combination of Fenretinide and Lenalidomide Shows Marked Antitumor Activity in a Neuroblastoma Xenograft Model
- PMID: 31908416
- PMCID: PMC6930389
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S221909
A Novel Nanomicellar Combination of Fenretinide and Lenalidomide Shows Marked Antitumor Activity in a Neuroblastoma Xenograft Model
Abstract
Purpose: Currently >50% of high-risk neuroblastoma (NB) patients, despite intensive therapy and initial partial or complete response, develop recurrent NB due to the persistence of minimal residual disease (MRD) that is resistant to conventional antitumor drugs. Indeed, their low therapeutic index prevents drug-dose escalation and protracted administration schedules, as would be required for MRD treatment. Thus, more effective and less toxic therapies are urgently needed for the management of MRD. To address this aim, we evaluated a new combination of fenretinide and lenalidomide, both endowed with antitumor activity and low-toxicity profiles. New nanomicelles were prepared as carriers for this combination to maximize bioavailability and accumulation at the tumor site because of the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect.
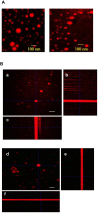
Experimental design: New nanomicelles containing the fenretinide-lenalidomide combination (FLnMs) were prepared by a one-step method, providing high drug encapsulation and micelle dimensions suitable for tumor accumulation. Their administration to mice bearing human NB xenografts allowed us to evaluate their efficacy in comparison with the nanomicelles containing fenretinide alone (FnMs).
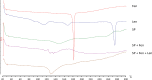
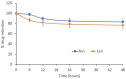
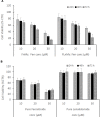
Results: Treatment by FLnMs significantly decreased the tumor growth of NB xenografts. FLnMs were more active than FnMs despite comparable fenretinide concentrations in tumors, and lenalidomide alone did not show cytotoxic activity in vitro against NB cells. The tumor mass at the end of treatment with FLnMs was predominantly necrotic, with a decreased Ki-67 proliferation index.
Conclusion: FLnMs provided superior antitumor efficacy in NB xenografts compared to FnMs. The enhanced efficacy of the combination was likely due to the antiangiogenic effect of lenalidomide added to the cytotoxic effect of fenretinide. This new nanomicellar combination is characterized by a low-toxicity profile and offers a novel therapeutic option for the treatment of high-risk tumors where the persistence of MRD requires repeated administrations of therapeutic agents over long periods of time to avoid recurrent disease.
Keywords: drugs combination; fenretinide; lenalidomide; nanomicelles; neuroblastoma.
© 2019 Orienti et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nanomicellar Lenalidomide-Fenretinide Combination Suppresses Tumor Growth in an MYCN Amplified Neuroblastoma Tumor.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Sep 16;15:6873-6886. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S262032. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32982239 Free PMC article.
-
The combined therapeutic effects of bortezomib and fenretinide on neuroblastoma cells involve endoplasmic reticulum stress response.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Feb 15;15(4):1199-209. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2477. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19228726
-
P450 inhibitor ketoconazole increased the intratumor drug levels and antitumor activity of fenretinide in human neuroblastoma xenograft models.Int J Cancer. 2017 Jul 15;141(2):405-413. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30706. Epub 2017 May 9. Int J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28340497
-
Immunoliposomal fenretinide: a novel antitumoral drug for human neuroblastoma.Cancer Lett. 2003 Jul 18;197(1-2):151-5. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(03)00097-1. Cancer Lett. 2003. PMID: 12880975 Review.
-
Clinical development of fenretinide as an antineoplastic drug: Pharmacology perspectives.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Jun;242(11):1178-1184. doi: 10.1177/1535370217706952. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 28429653 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Revolution in Cancer Treatment: How Are Intelligently Designed Nanostructures Changing the Game?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 9;25(10):5171. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105171. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomicellar Lenalidomide-Fenretinide Combination Suppresses Tumor Growth in an MYCN Amplified Neuroblastoma Tumor.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Sep 16;15:6873-6886. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S262032. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32982239 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging therapeutic targets for neuroblastoma.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020 Sep;24(9):899-914. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2020.1790528. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020. PMID: 33021426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulmonary Delivery of Fenretinide: A Possible Adjuvant Treatment In COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 27;21(11):3812. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113812. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32471278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retinoid Therapy for Neuroblastoma: Historical Overview, Regulatory Challenges, and Prospects.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 26;16(3):544. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030544. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339295 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Garaventa A, Luksch R, Lo Piccolo MS, et al. Phase I trial and pharmacokinetics of fenretinide in children with neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9(6):2032–2039. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

