AR-42: A Pan-HDAC Inhibitor with Antitumor and Antiangiogenic Activities in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 31908417
- PMCID: PMC6930838
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S211665
AR-42: A Pan-HDAC Inhibitor with Antitumor and Antiangiogenic Activities in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is a refractory malignancy with high morbidity and mortality. Thus, there is an urgent need to find effective targets and agents for ESCC treatment. The purpose of this study was to assess the anti-ESCC effects of a pan-histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor AR-42 and its mechanisms of action.
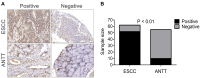
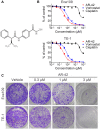
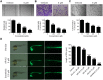
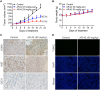
Methods: Immunohistochemical staining was performed to detect HDAC1 expression in ESCC and adjacent tissue samples. MTT assay, Edu cell proliferation test, flow cytometry, and subcutaneous xenograft were used to assess the anti-ESCC effects of AR-42; furthermore, the antiangiogenic activity of AR-42 was evaluated using endothelial cell migration, invasion, and tube formation assays as well as zebrafish angiogenesis assay. Western blot analysis was performed to explore the underlying mechanism of the anti-ESCC activity of AR-42.
Results: HDAC1-positive expression was much higher in ESCC cells than in paracancerous tissues, and the elevated HDAC1 expression was a strong indicator of lymph node metastasis and a more advanced TNM stage of ESCC. Moreover, AR-42 potently suppressed ESCC cell growth through cellular proliferation inhibition and apoptosis induction. Moreover, AR-42 displayed a moderate antiangiogenic activity, and it could significantly inhibit the migration, invasion and tubulogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells as well as intersegmental vessel formation in zebrafish at micromolar concentrations. More importantly, the inhibitory activity of AR-42 on ESCC cells and angiogenesis could also be observed in the TE-1 xenograft model. Further studies showed that AR-42 exerts its anti-ESCC effects mainly by upregulating the expression of p21 and blocking the transduction of multiple signaling cascades related to tumor growth, especially Stat3-mediated signaling.
Conclusion: Overall, AR-42 has significant potency for inhibiting ESCC cell growth and shows moderate effect in suppressing angiogenesis, displaying strong anti-ESCC effects in vitro and in vivo. Thus, AR-42 deserves further evaluation as a potential candidate for ESCC therapy.
Keywords: AR-42; angiogenesis; esophageal squamous cell cancer; histone deacetylase.
© 2019 Zhu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Alkannin Induces G2/M-Phase Arrest, Apoptosis, and Inhibition of Invasion by Targeting GSK3β in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Nov 25;18:5377-5395. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S470061. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39618426 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudolaric Acid B Inhibits Proliferation, Invasion, and Angiogenesis in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Through Regulating CD147.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Oct 28;14:4561-4573. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S269915. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 33149553 Free PMC article.
-
Corilagin Inhibits Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Inducing DNA Damage and Down-Regulation of RNF8.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019;19(8):1021-1028. doi: 10.2174/1871520619666190307120811. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30848215
-
Development of targeted therapy of NRF2high esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Cell Signal. 2021 Oct;86:110105. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110105. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Cell Signal. 2021. PMID: 34358647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems: opportunities and challenges in the treatment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).Nanoscale. 2025 Apr 3;17(14):8270-8288. doi: 10.1039/d4nr05114a. Nanoscale. 2025. PMID: 40052671 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanism, regulation, and therapeutic targeting of the STAT3 signaling pathway in esophageal cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2022 Sep;61(3):105. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2022.5395. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Int J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35856449 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of prognostic risk model and drug sensitivity based on prognostic related genes of esophageal cancer.Sci Rep. 2022 May 14;12(1):8008. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11760-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35568702 Free PMC article.
-
MST1 interactomes profiling across cell death in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Med Rev (2021). 2024 Jun 14;4(6):531-543. doi: 10.1515/mr-2024-0031. eCollection 2024 Dec. Med Rev (2021). 2024. PMID: 39664081 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights into the LANCL2-ABA Binding Mode towards the Evaluation of New LANCL Agonists.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Dec 12;15(12):2754. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15122754. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38140095 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-tumour activity of Panobinostat in oesophageal adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma cell lines.Clin Epigenetics. 2024 Aug 3;16(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s13148-024-01700-3. Clin Epigenetics. 2024. PMID: 39097736 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

